
Human Appendix Anatomy, Location and Function of Appendix
The normal fatty meso-appendix can be identified if outlined by some intraperitoneal fluid as in this patient, and is moderately hyperechoic, soft and well-compressible. Roughly 4-6 hours after the onset of symptoms, the inflammation begins to affect the meso-appendix, which becomes larger, more hyperechoic and non-compressible (arrowheads).
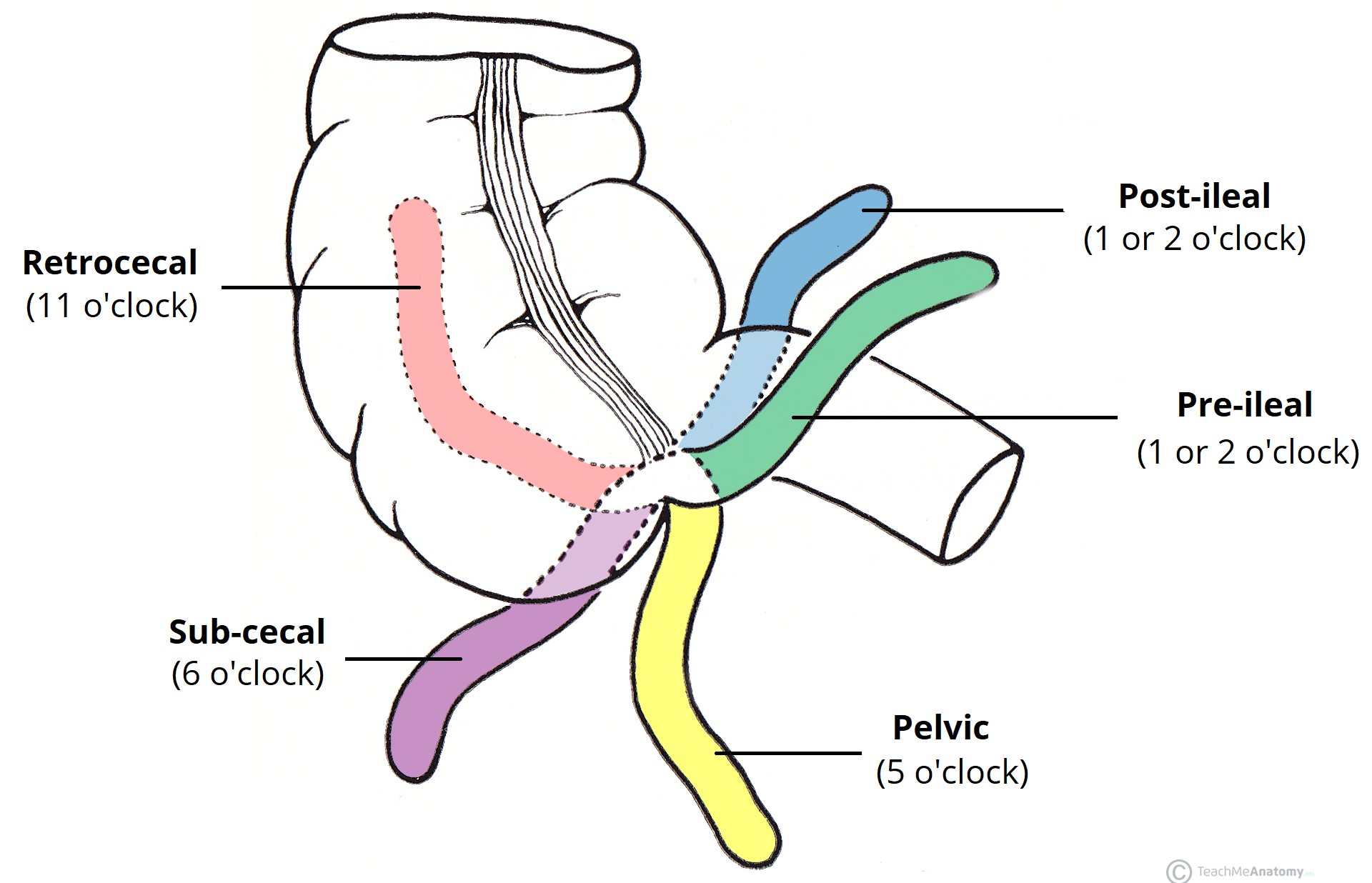
The Appendix Retrocecal Arterial supply Appendicitis TeachMeAnatomy
Normal Appendix . The appendix is a small, hollow, finger-shaped organ attached to the first part of the large intestine on the lower right side of the abdomen. The appendix is filled with lymph (a clear fluid that carries infection-fighting cells) and has its own blood and nerve supply.

How To Find The Appendix On Imaging Stepwards
In addition, a MMT < 3 mm should be regarded as normal in children less than 6 years old. Wiersma et al [ 10] also reported that the sizes of the MOD and the MMT in a normal appendix in children was 0.21-0.64 cm and 0.11-0.27 cm, respectively. Go to:
Human Appendix Anatomy, Location and Function of Appendix
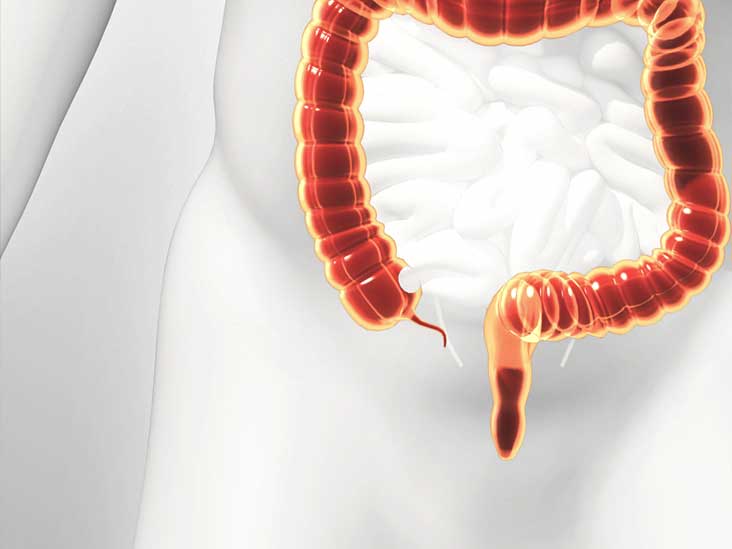
The appendix is a finger-shaped pouch that sticks out from the colon on the lower right side of the belly, also called the abdomen. Appendicitis causes pain in the lower right abdomen. However, in most people, pain begins around the belly button and then moves. As inflammation worsens, appendicitis pain typically increases and eventually.
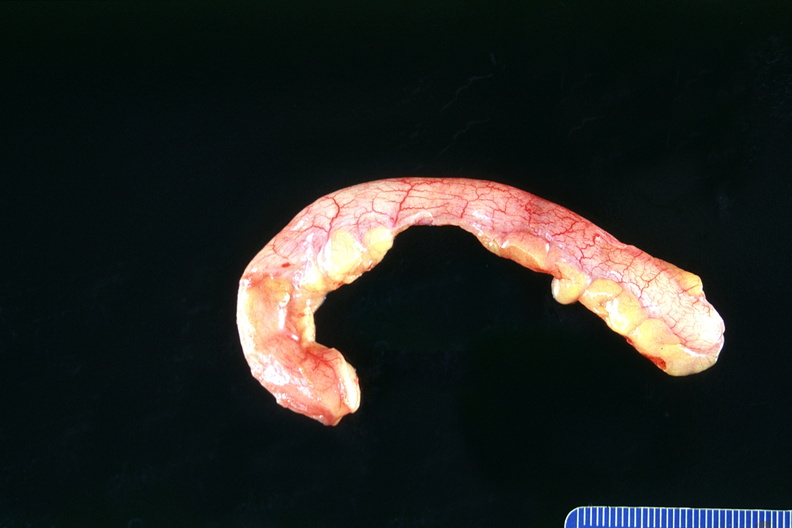
00017030 PEIR Digital Library
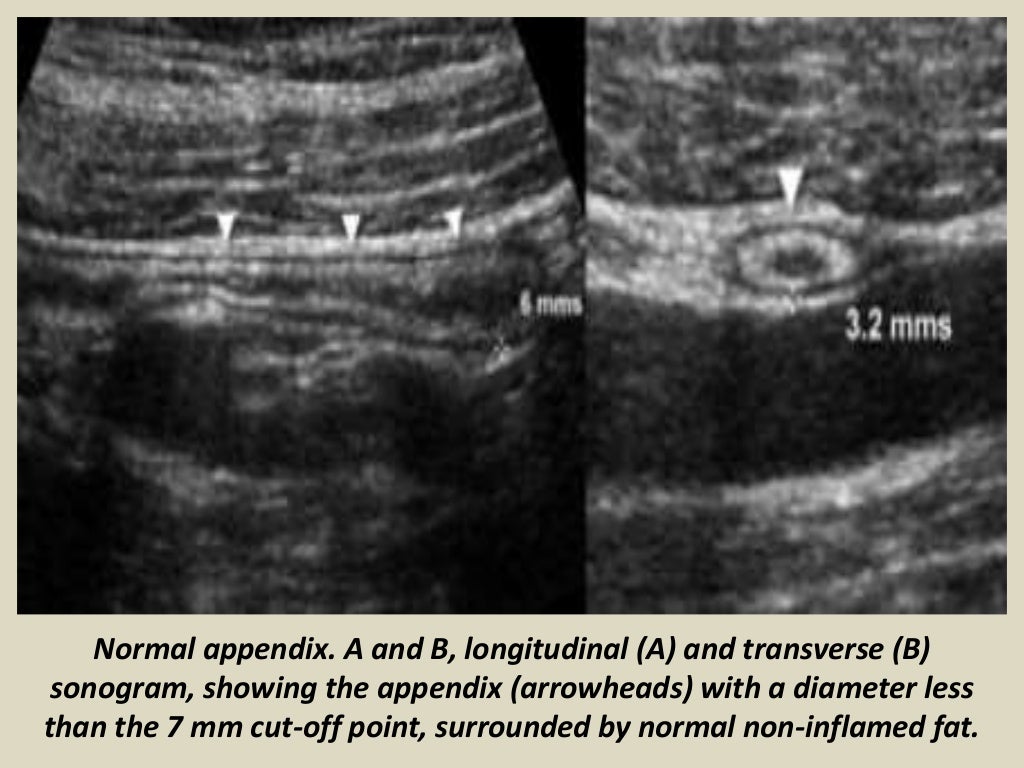
The normal diameter of the appendix can be as high as 12.8 mm. 91.5% of normal appendices are larger than 6 mm in our study. The normal wall thickness is larger than 3 mm in 8% of normal appendixes. Hence, relying on appendix size alone may lead to misdiagnosis and mismanagement.
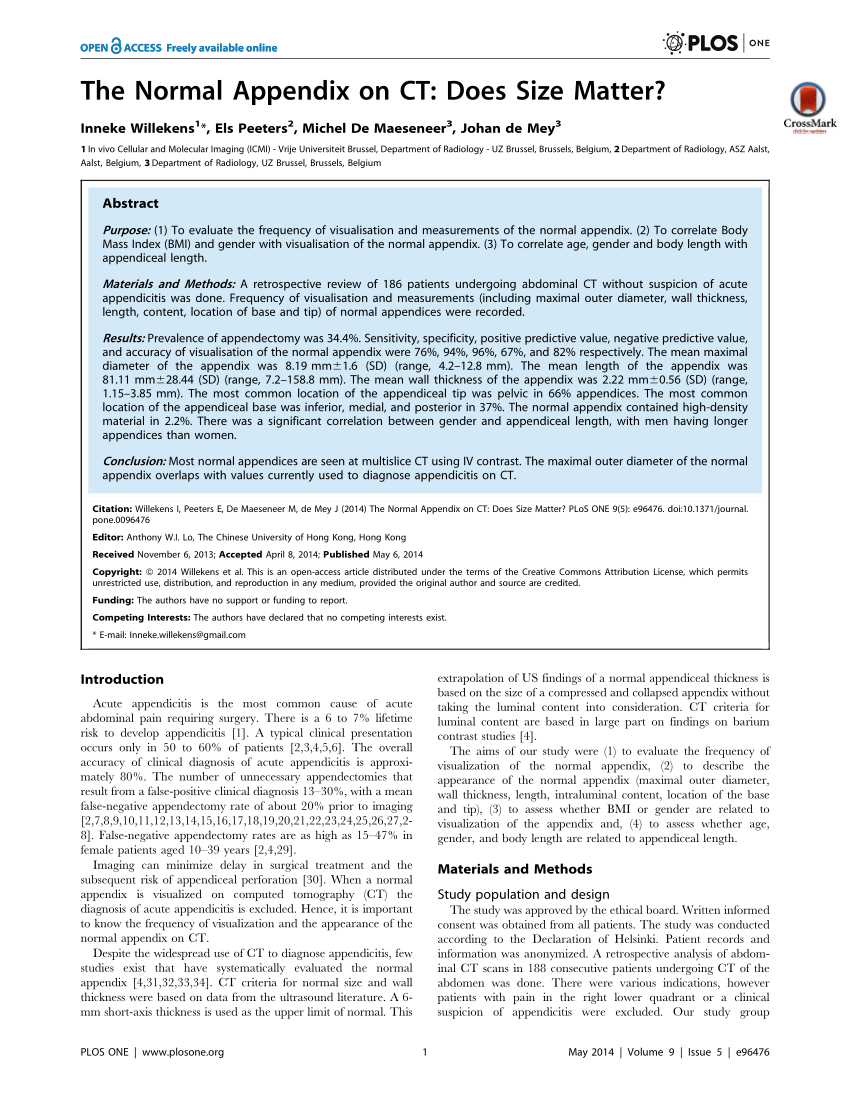
(PDF) The Normal Appendix on CT Does Size Matter?
RESULTS. The mean maximum depth of the intraluminal appendiceal fluid in the appendicitis group was significantly higher than in the two groups with a normal appendix (Mann-Whitney U test: p < 0.001). When using maximum depth of the intraluminal appendiceal fluid greater than 2.6 mm for a criterion of appendicitis, sensitivity and specificity for differentiation between the appendicitis group.

Longitudinal view of the normal appendix shows maximal axial outer... Download Scientific Diagram
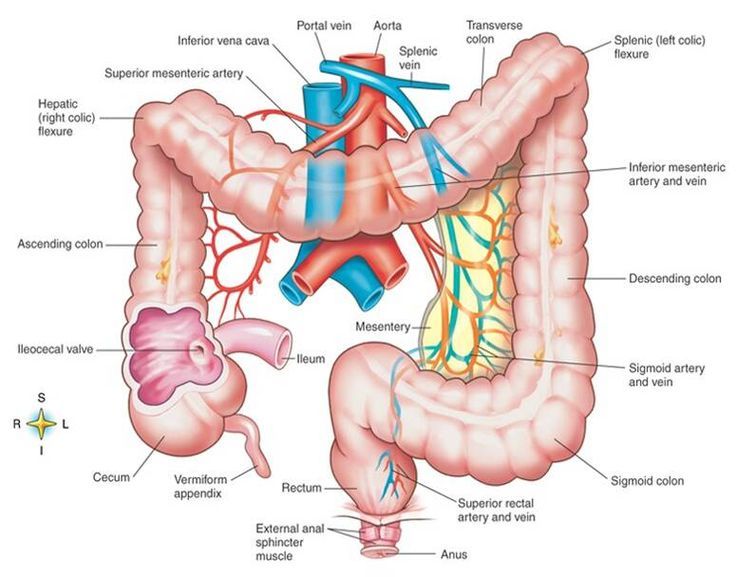
The appendix arises from the posteromedial surface of the cecum, approximately 2-3 cm inferior to the ileocecal valve, where the three longitudinal bands of the taeniae coli converge. It is a blind diverticulum which is highly variable in length, ranging between 2 and 20 cm. The appendiceal mesentery is called the mesoappendix 1,2.

Scientists Have Finally Discover the Function of the Human Appendix HEA. Tube YouTube
Appendicitis should not be diagnosed by size alone. Normal appendices can measure 13 mm in width and 35 cms in length, so it is important to consider the ancillary findings of obstruction, ischemia, inflammation and perforation.. However, the identification of a normal appendix is less consistent, and in many instances, appendicitis cannot.

Normal Appendix 100x (insert 200x) Histology Slides, Protein, Appendix, Medical Laboratory
The normal caliber of a collapsed appendix on computed tomography (CT) is generally accepted as ≤ 6 mm and can be identified in 43-100% of patients depending on factors such as contrast enhancement and slice thickness (Figs. 3a, b) [].However, if distended by air or contrast material, a normal appendix can measure up to 10 mm.
What Does the Appendix Do?
Among these patients, the mean diameter of the normal appendix was 5.6-5.7 mm, with a normal range (95% CI) encompassing 2.7-8.7 mm and 34-39% of normal appendixes measuring greater than 6 mm in diameter. Although this represents a much larger sample than prior studies, the mean normal appendiceal diameter is concordant with diameters.
Appendix Location, Function, Anatomy and FAQs
Appendicitis is an inflamed appendix. It can cause acute (sudden, intense) pain in your lower abdomen. Your appendix is a small, tubular pouch, about the size of a finger, that protrudes from the lower right end of your large intestine. Poop (feces) moving through your large intestine can block or infect your appendix, leading to inflammation.
Presentation1.pptx, ultrasound examination of the appendix.
The appendix is a narrow blind-ended tube that is attached to the posteromedial end of the cecum (large intestine). It contains a large amount of lymphoid tissue but is not thought to have any vital functions in the human body.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the appendix - its anatomical structure and relations, neurovascular supply and lymphatic drainage.

Bipolar Normalorwhatever 2
Clinical evaluation — The diagnostic accuracy of the clinical evaluation for acute appendicitis depends on the experience of the examining clinician [ 2-7 ]. The patient presenting with acute abdominal pain should undergo a thorough physical examination, including a digital rectal examination. Women should undergo a pelvic examination.
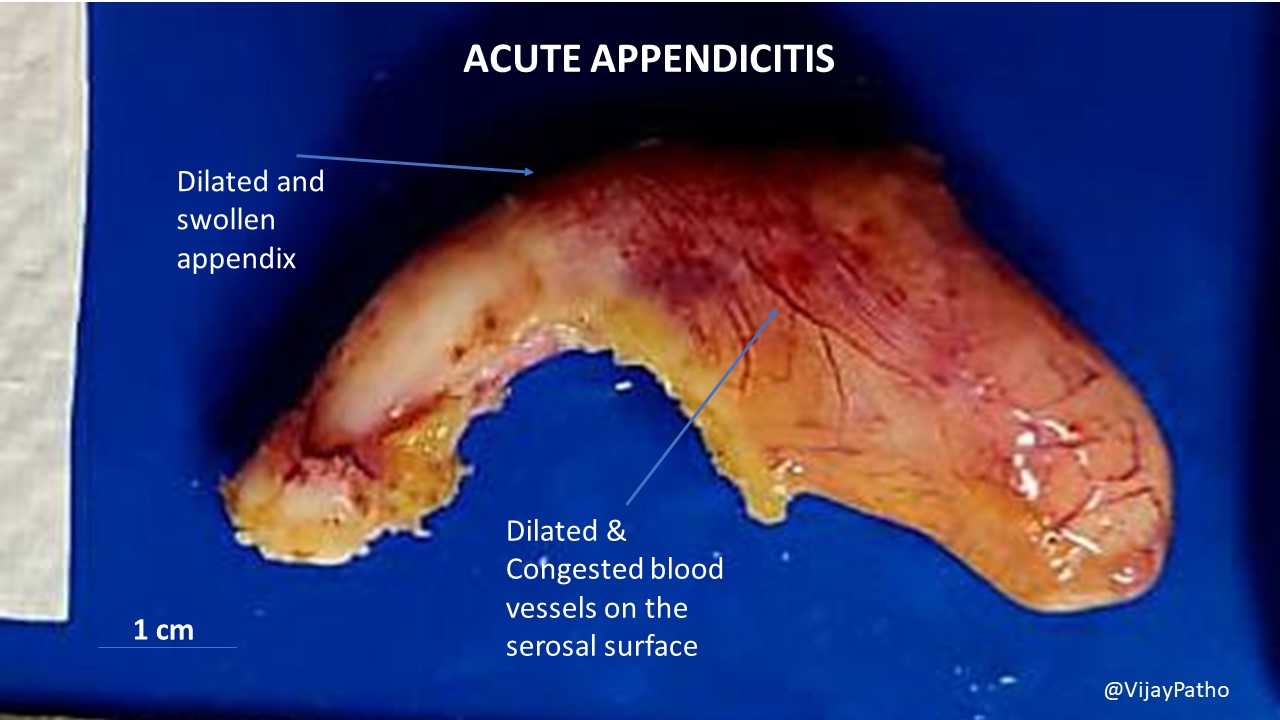
ACUTE APPENDICITIS Pathology Made Simple
Appendicitis should not be diagnosed by size alone. Normal appendices can measure 13 mm in width and 35 cms in length, so it is important to consider the ancillary findings of obstruction, ischaemia, inflammation and perforation.. However, the identification of a normal appendix is less consistent, and in many instances, appendicitis cannot.

Appendix Positions Retrocecal (*most common) GrepMed
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of the present study is to assess the visibility of the normal appendix on CT, MRI, or ultrasound (US) images of a healthy population. MATERIALS AND METHODS. The MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched to identify articles on the rates of detection of a normal appendix on CT, MRI, or US that appeared in the literature published up to January 20, 2017. Pooled detection.

CT appearance of the normal appendix in adults Semantic Scholar
The normal diameter of the appendix can be as high as 12.8 mm. 91.5% of normal appendices are larger than 6 mm in our study. The normal wall thickness is larger than 3 mm in 8% of normal appendixes. Hence, relying on appendix size alone may lead to misdiagnosis and mismanagement.
- 10 Am Eastern Daylight Time
- Whats On In Mackay This Weekend
- I Want To In French
- Black Pearl Cookie Voice Lines
- James Acaster S Guide To Quitting Social Media
- Module 17 Challenge Penetration Test Report
- Australian Map With States And Capital Cities
- Country Life Roxy Music Album
- 10 Myall Ave Murray Bridge
- How Many Weeks Until June 30