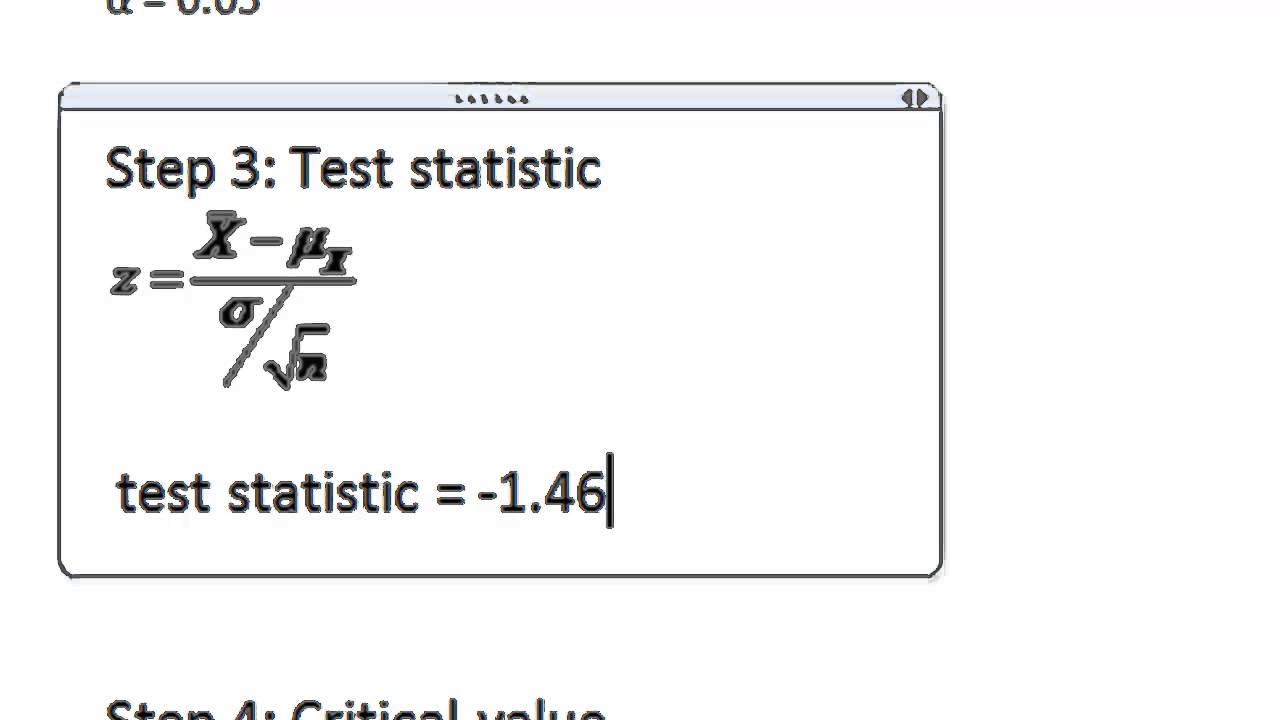
Stats Hypothesis Testing using Critical Value Example YouTube
A statistical test is a tool or procedure used in data analysis to determine the likelihood of observing certain patterns, relationships, or differences in a dataset by chance alone. It helps researchers draw conclusions about the population based on sample data. Statistical tests involve mathematical calculations and hypothesis testing to.
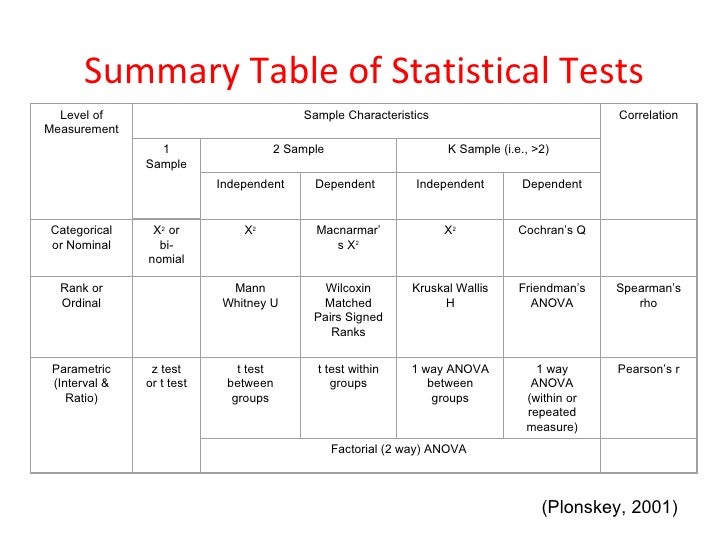
T11 types of tests
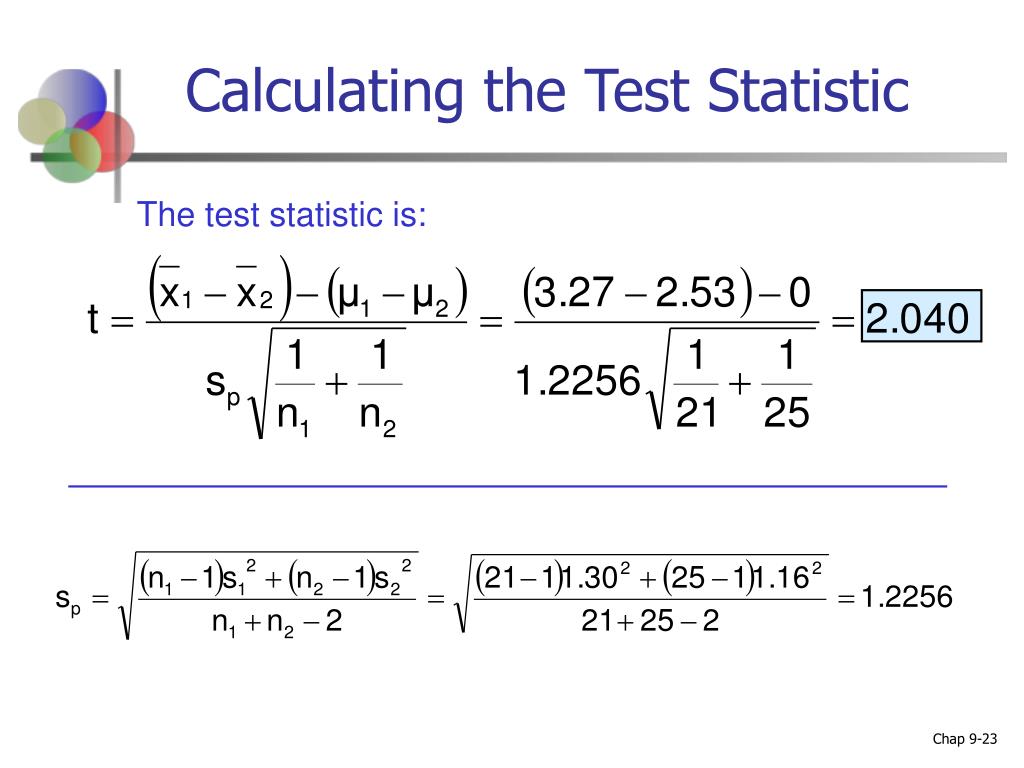
Test statistic is a quantity derived from the sample for statistical hypothesis testing. [1] A hypothesis test is typically specified in terms of a test statistic, considered as a numerical summary of a data-set that reduces the data to one value that can be used to perform the hypothesis test. In general, a test statistic is selected or.
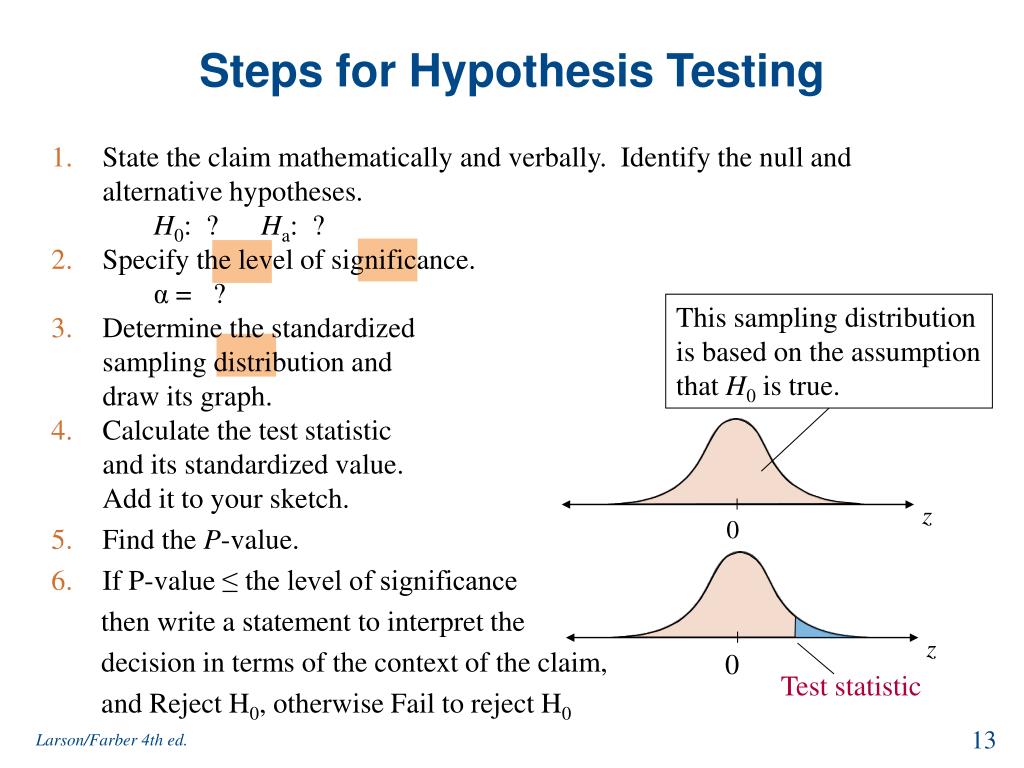
PPT Ch7 Hypothesis Testing (1 Sample) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5096598
The STAT is an aptitude test that assesses a range of competencies considered important for tertiary study. STAT Multiple Choice is the version used by SATAC's partner institutions. It is a two-hour test evaluating skills associated with verbal and quantitative reasoning. STAT Written English is not used for entry to courses offered through SATAC.

Statistical Test Guide to Compare Groups Prof Paresh Shah
A statistical test provides a mechanism for making quantitative decisions about a process or processes. The intent is to determine whether there is enough evidence to "reject" a conjecture or hypothesis about the process. The conjecture is called the null hypothesis. Not rejecting may be a good result if we want to continue to act as if we.
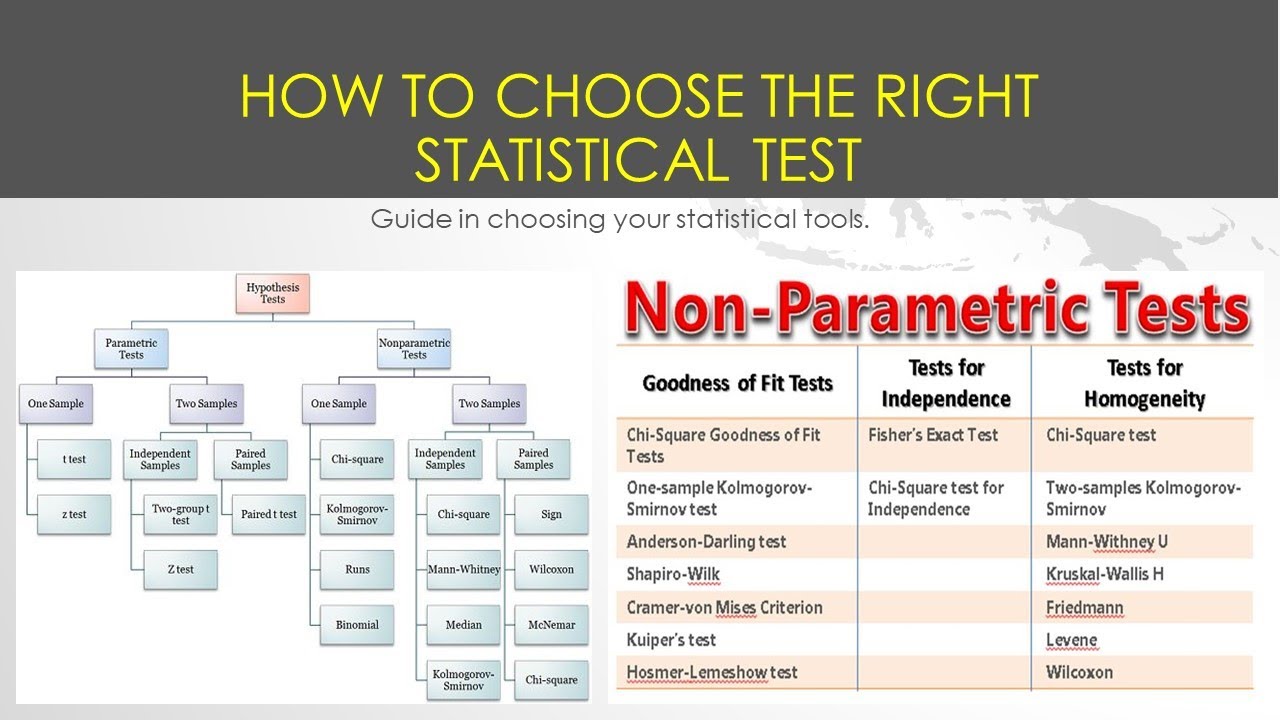
Guide on How to Choose the Right Statistical Test YouTube
Hi Jim. I used the one-tailed(right) statistical test to determine an anomaly in the below problem statement: On a daily basis, I calculate the (mapped_%) in a common field between two tables. The way I used the t-test is: On any particular day, I calculate the sample_mean, S.D and sample_count (n=30) for the last 30 days including the current day.

What is a Standardized Test Statistic? Statology
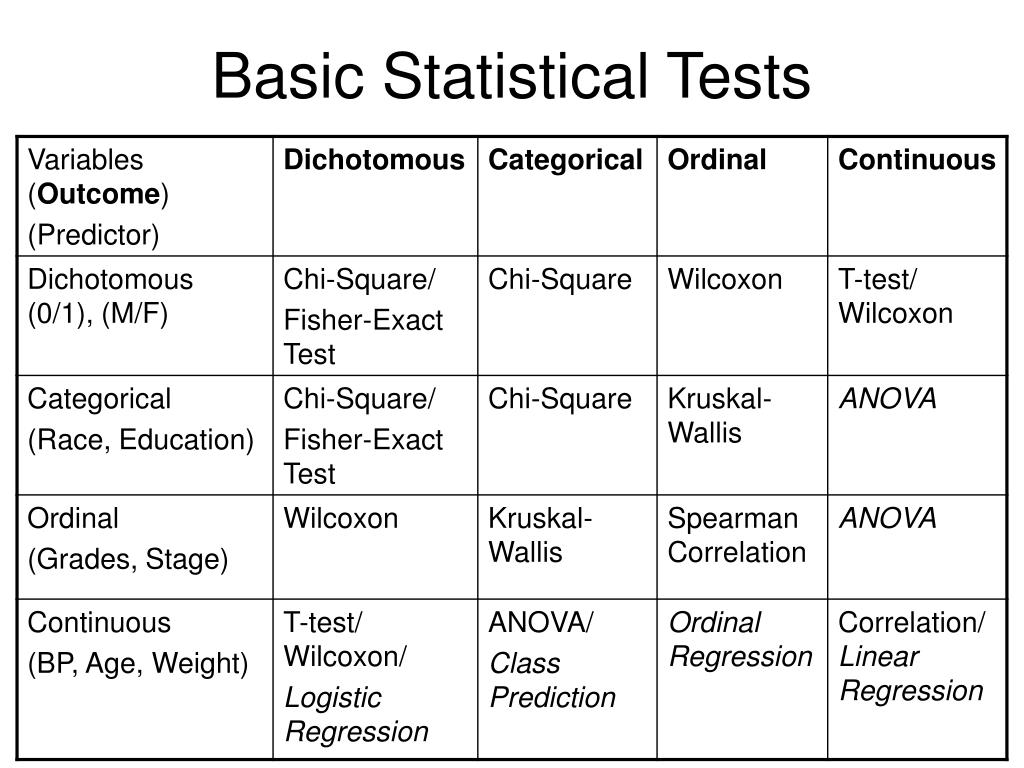
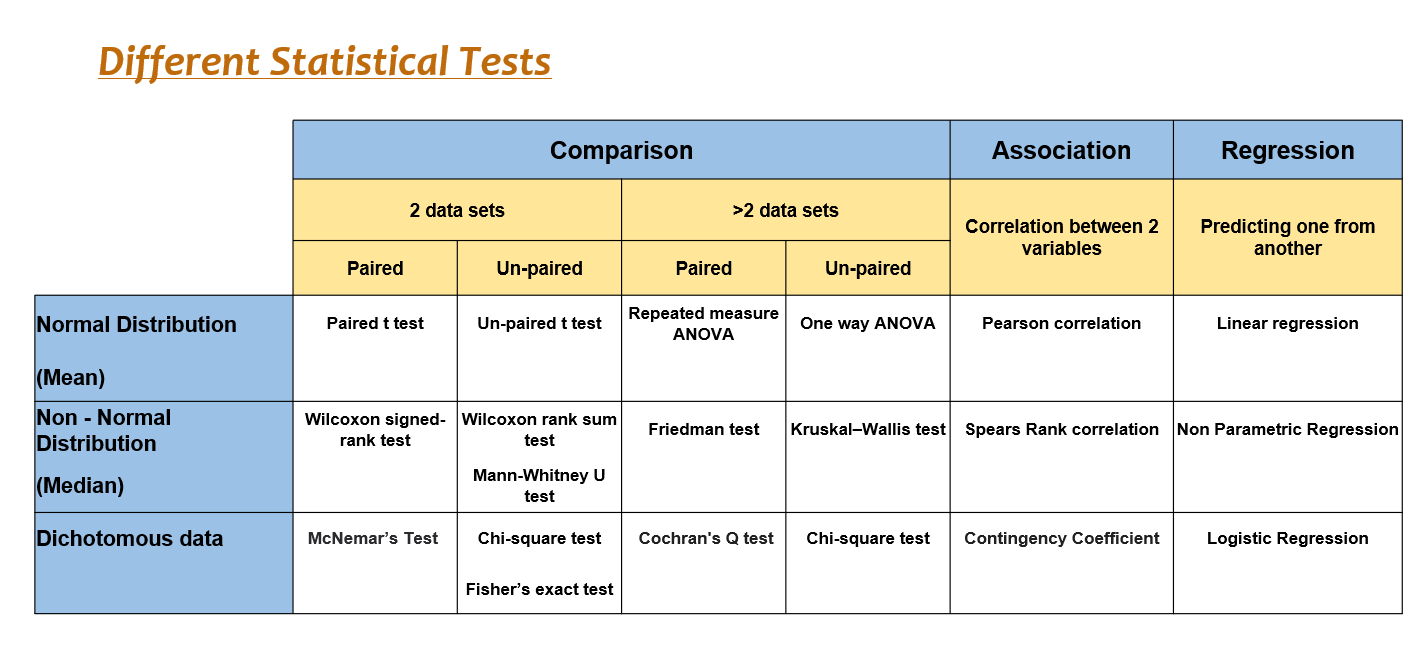
Finding the appropriate statistical test is easy if you're aware of. the measurement levels of the variables involved. For each type and measurement level, this tutorial immediately points out the right statistical test. We'll also briefly define the 6 basic types of tests and illustrate them with simple examples. 1.
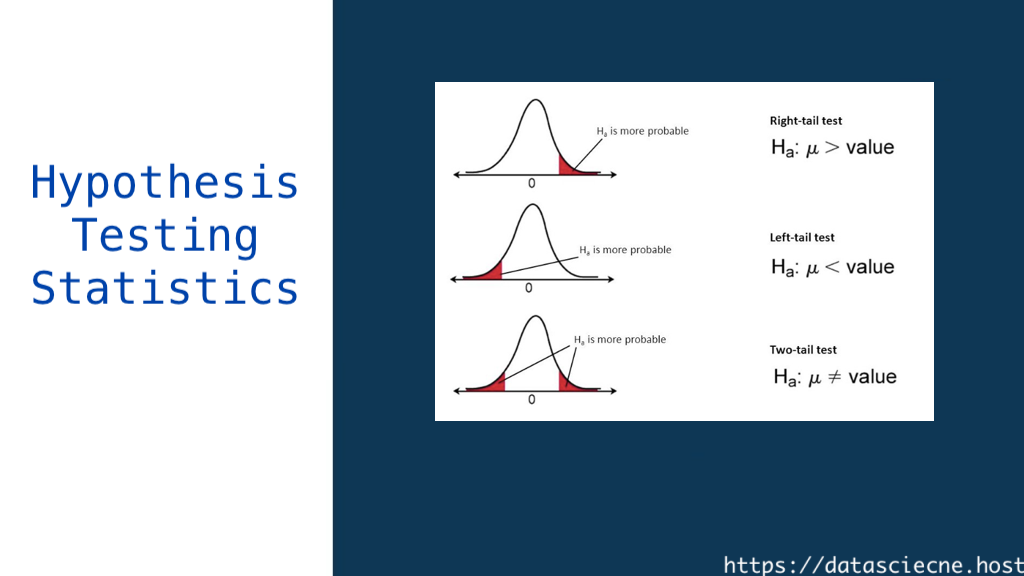
Hypothesis Testing Statistics
When to perform a statistical test. You can perform statistical tests on data that have been collected in a statistically valid manner - either through an experiment, or through observations made using probability sampling methods.. For a statistical test to be valid, your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.
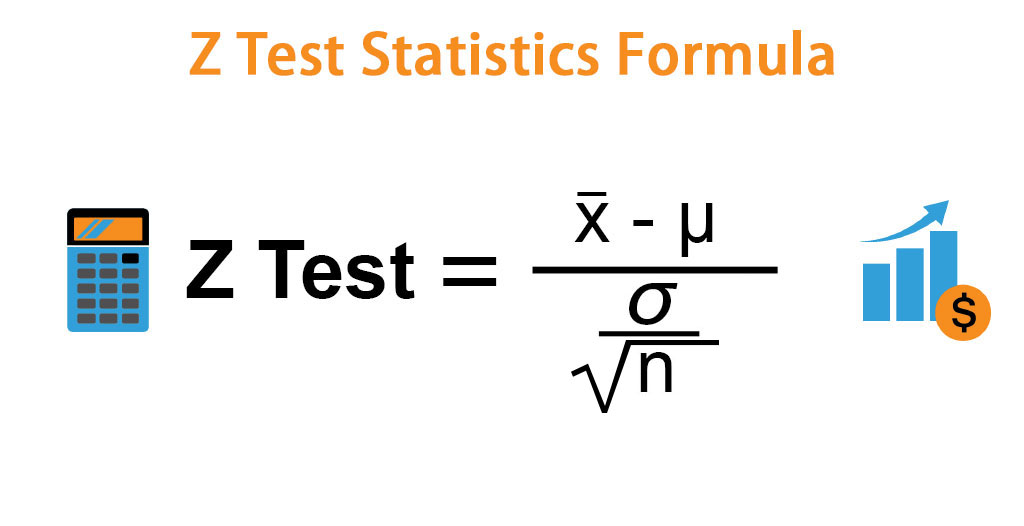
Z Test Statistics Formula Calculator (Examples With Excel Template)
Test statistics represent effect sizes in hypothesis tests because they denote the difference between your sample effect and no effect —the null hypothesis. Consequently, you use the test statistic to calculate the p-value for your hypothesis test. The above p-value definition is a bit tortuous.
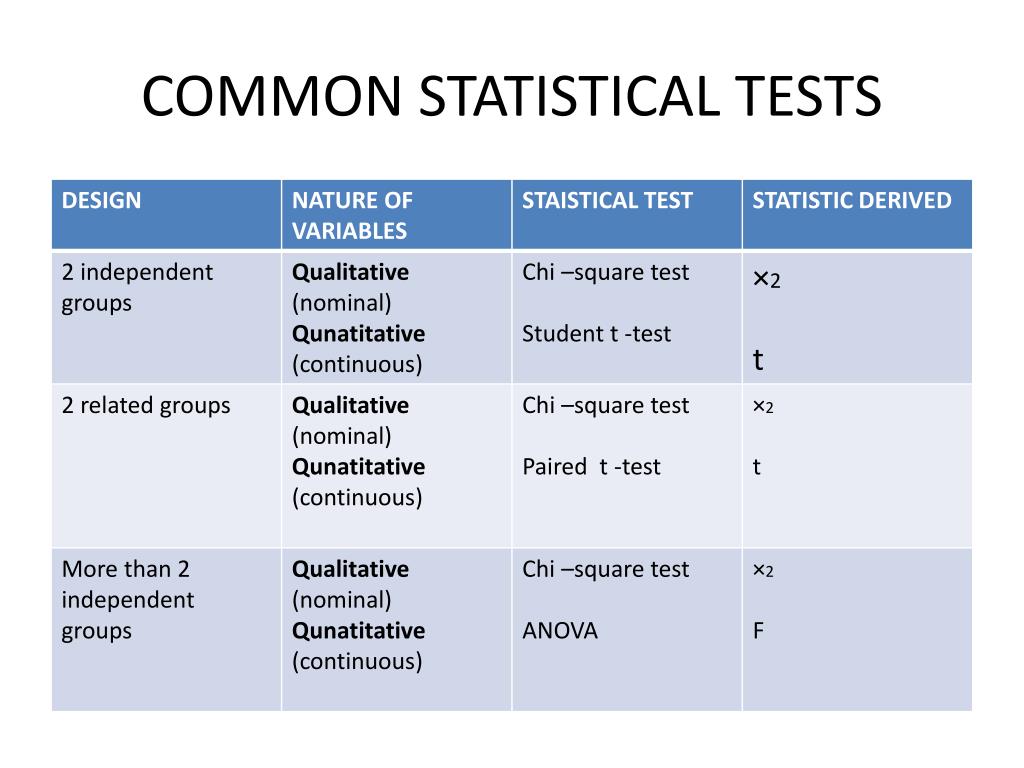
PPT TESTS OF STATISTICAL SIGNIFICANCE PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5793209
T-Test is a method used in statistics to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two groups and how they are related. In T-Test statistics, the sample data is a subset of the two groups that we use to draw conclusions about the groups as a whole.
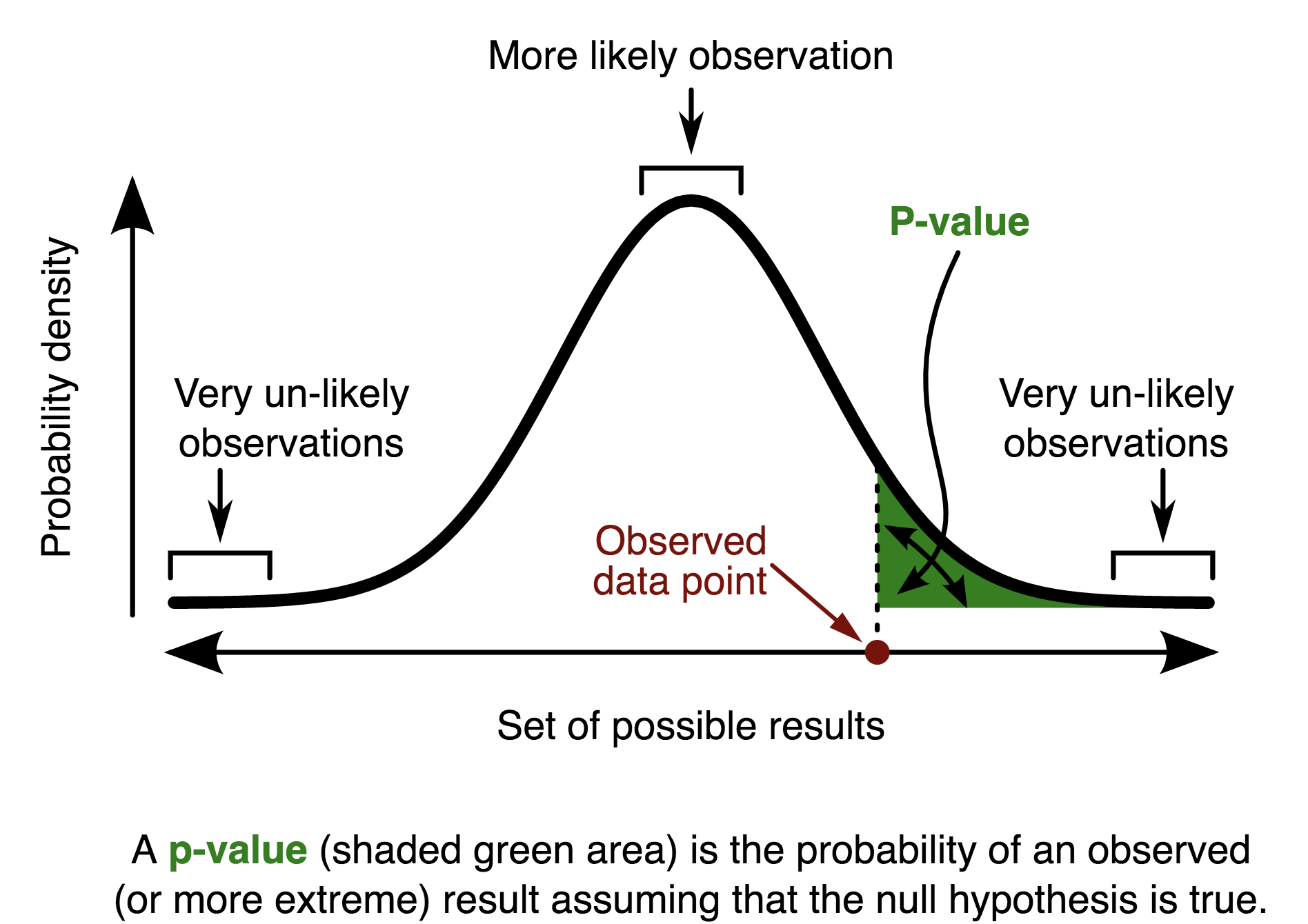
Test a Hypothesis Design Effective Statistical Models to Understand Your Data OpenClassrooms
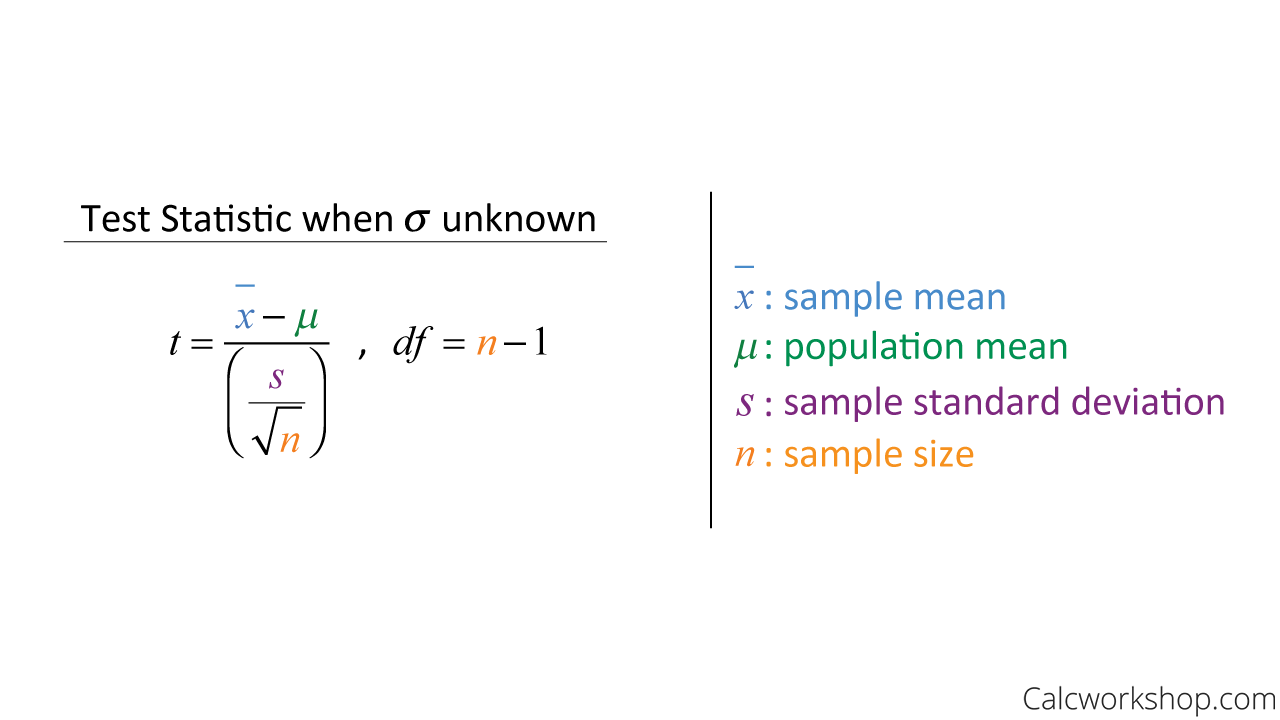
T Distribution Calculator. The t distribution calculator makes it easy to compute the cumulative probability associated with a t score or with a sample mean. For help in using the calculator, read the Frequently-Asked Questions or review the Sample Problems.. To learn more about Student's t distribution, go to Stat Trek's tutorial on the t distribution.
PPT Medical Statistics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2976758
Statistical errors. With two hypotheses, there are four possible outcomes (Table 5.1.1 5.1. 1 ). The first (a) and the last (d) outcomes are ideal cases: we either accept the null hypothesis which is correct for the population studied, or we reject H0 H 0 when it is wrong. If we have accepted the alternative hypothesis, when it is not true, we.
PPT Chapter 9 Estimation and Hypothesis Testing for Two Population Parameters PowerPoint
Stat testing, short for "statistical testing" or "urgent testing," is a category of medical testing that prioritizes speed and efficiency in delivering results. It is reserved for situations where a healthcare provider requires test results as quickly as possible to make immediate clinical decisions. Stat tests are typically associated with.

ACT, NSW, TAS & VIC STAT Mentors
Use a one-sample t test to compare a sample mean to a reference value. It allows you to determine whether the population mean differs from the reference value. The reference value is usually highly relevant to the subject area. For example, a coffee shop claims their large cup contains 16 ounces. A skeptical customer takes a random sample of 10.

What statistical test should I use?
The choice of statistical test used for analysis of data from a research study is crucial in interpreting the results of the study. This article gives an overview of the various factors that determine the selection of a statistical test and lists some statistical testsused in common practice. How to cite this article: Ranganathan P. An.
One Sample T Test (Easily Explained w/ 5+ Examples!)
Test Statistic Explained. A test statistic is a value acquired after the hypothesis test on the sample data representing the entire population. The process of hypothesis testing starts with a null hypothesis (H0), which serves as the default or baseline assumption. Subsequently, a sample of data is collected, and a test statistic is computed based on this information.
How to choose statistical test for Analysis Dr Venugopala Rao Manneni
Z is the symbol for the Z-test statistic for population proportions. p ^ \hat{p} p ^ is the sample proportion. p 0 p_{0} p 0 is the hypothesized value of the population proportion according to the null hypothesis. n n n is the sample size . When your sample size is smaller than 30 (n30)—or when you cannot assume that the distribution of your sample statistic is normally distributed—you.