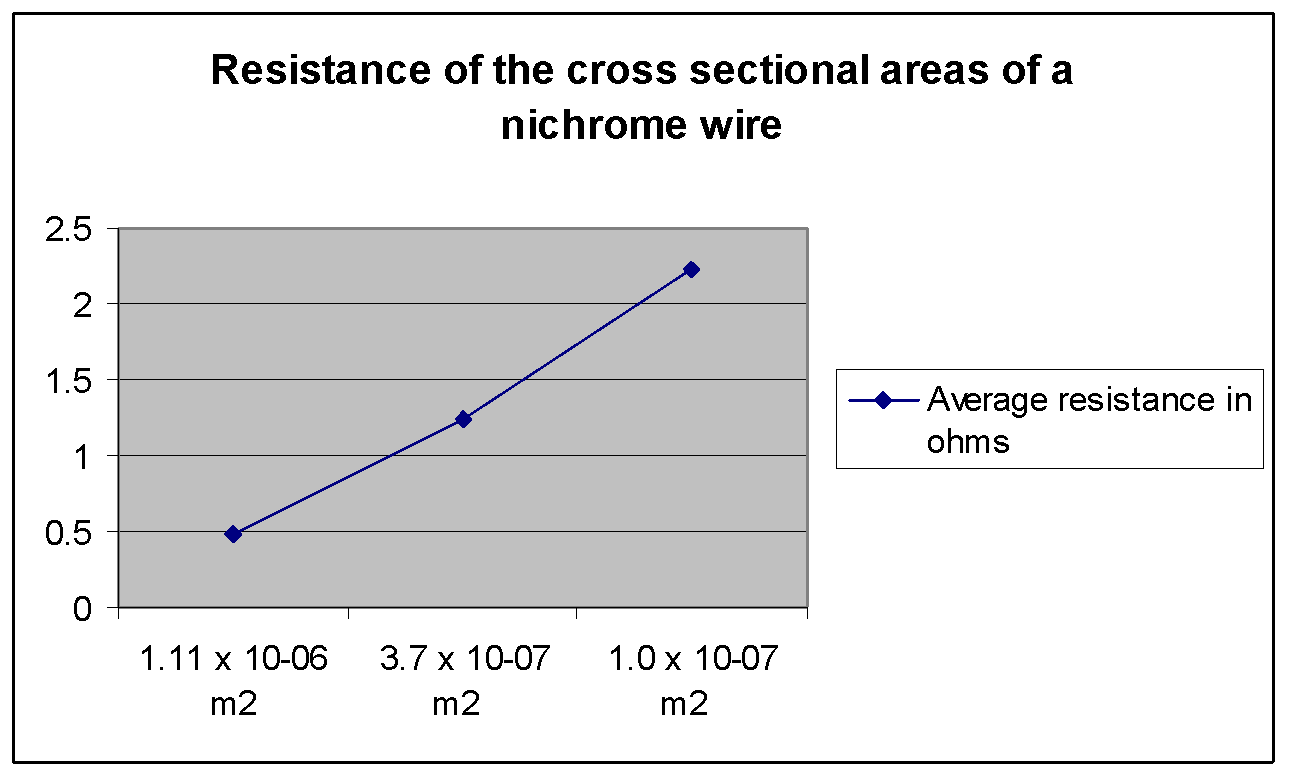
Investigate the effects of resistance on a nichrome wire GCSE Science Marked by
Data reproduced with permission of Granta Design Limited www.grantadesign.com. Nickel/chromium alloys have excellent oxidation resistance, wear-resistance and high-temperature properties. Typical applications include heating elements and thermocouples.
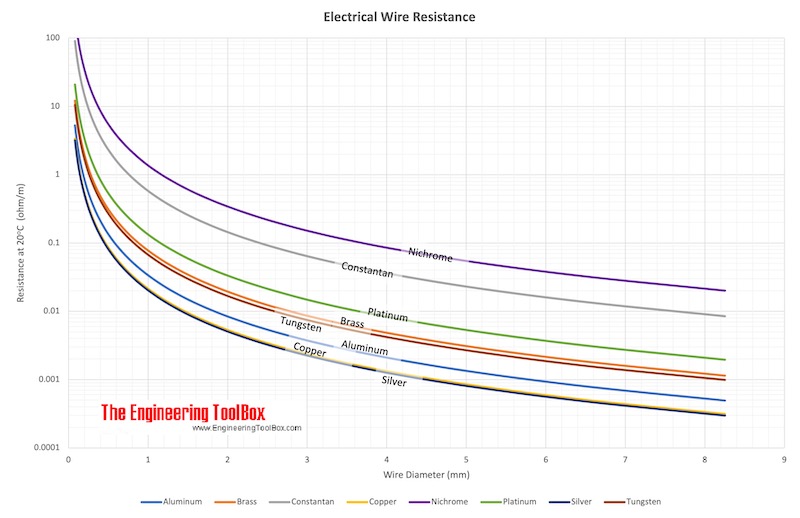
Electric Wire Resistance
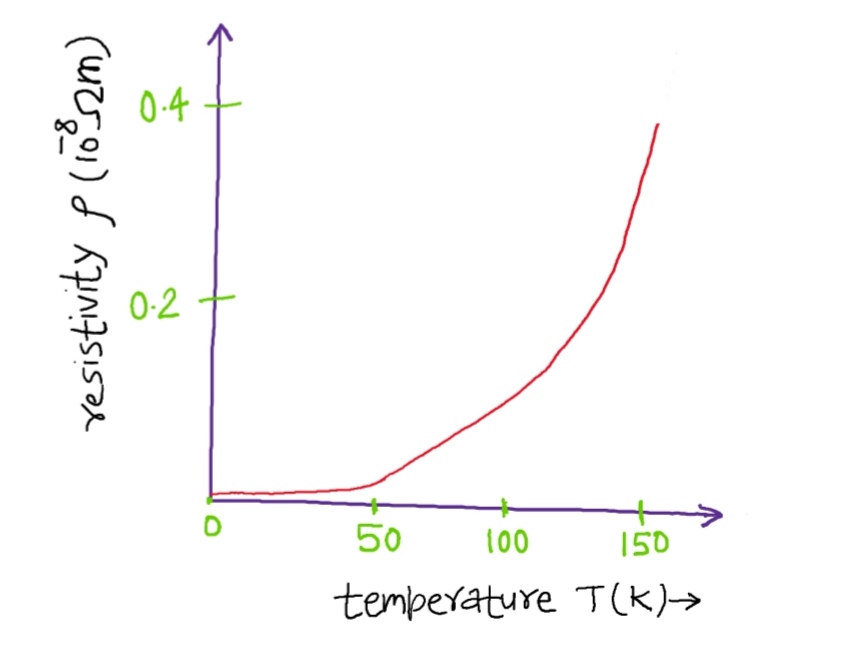
The nichrome wire undergoes a phase transition at that mysterious temperature which changes its unit cell structure. The two different unit cells have slightly different bulk resistivities. Superimposed on that shift is the usual increase in resistivity with temperature for metallic solids.
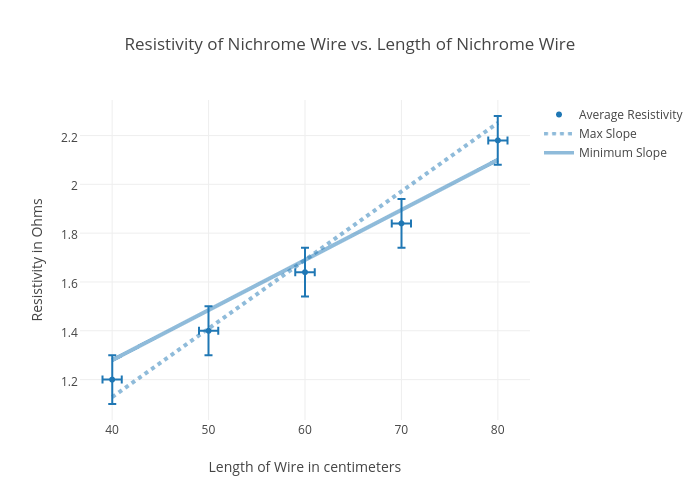
Resistivity of Nichrome Wire vs. Length of Nichrome Wire scatter chart made by Franciscoj1
In this video we take the formula for calculating the resistance of a conductor and transpose it to find a formula to calculate the resistivity of a material.

Physics Archive April 07, 2017
Nichrome has a silvery gray coloration. Specific gravity. The specific gravity of Nichrome is 8.4. Density. The density of Nichrome is 8400 kg/m 3. Melting point. The melting point of this substance is 1400°C. Electrical resistivity at room temperature. The electrical resistivity at room temperature for this substance is 1.0 × 10 −6 to 1.5.

Heating Elements Nickel Alloys
Types. Nichrome, a non-magnetic 80/20 alloy of nickel and chromium, is the most common resistance wire for heating purposes because it has a high resistivity and resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, up to 1,400 °C (2,550 °F).When used as a heating element, resistance wire is usually wound into coils. Kanthal (Alloy 875/815), a family of iron-chromium-aluminium (FeCrAl) alloys, is.
The varying of the resistance of nichrome wire depending on its length ALevel Science
*The resistivity of semiconductors depends strongly on the presence of impurities in the material, a fact which makes them useful in solid state electronics. References: 1. Giancoli, Douglas C., Physics, 4th Ed, Prentice Hall, (1995). 2. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 64th ed. 3. Wikipedia, Electrical resistivity and conductivity. 4.

Solved AIM To study the resistivity of Nichrome wire
Nichrome is basically a name given to nickel-chromium resistance wires. It is a non-magnetic alloy, which consists of 80 percent nickel and 20 percent chromium by weight, and is widely used in heating elements because of its relatively high resistivity.

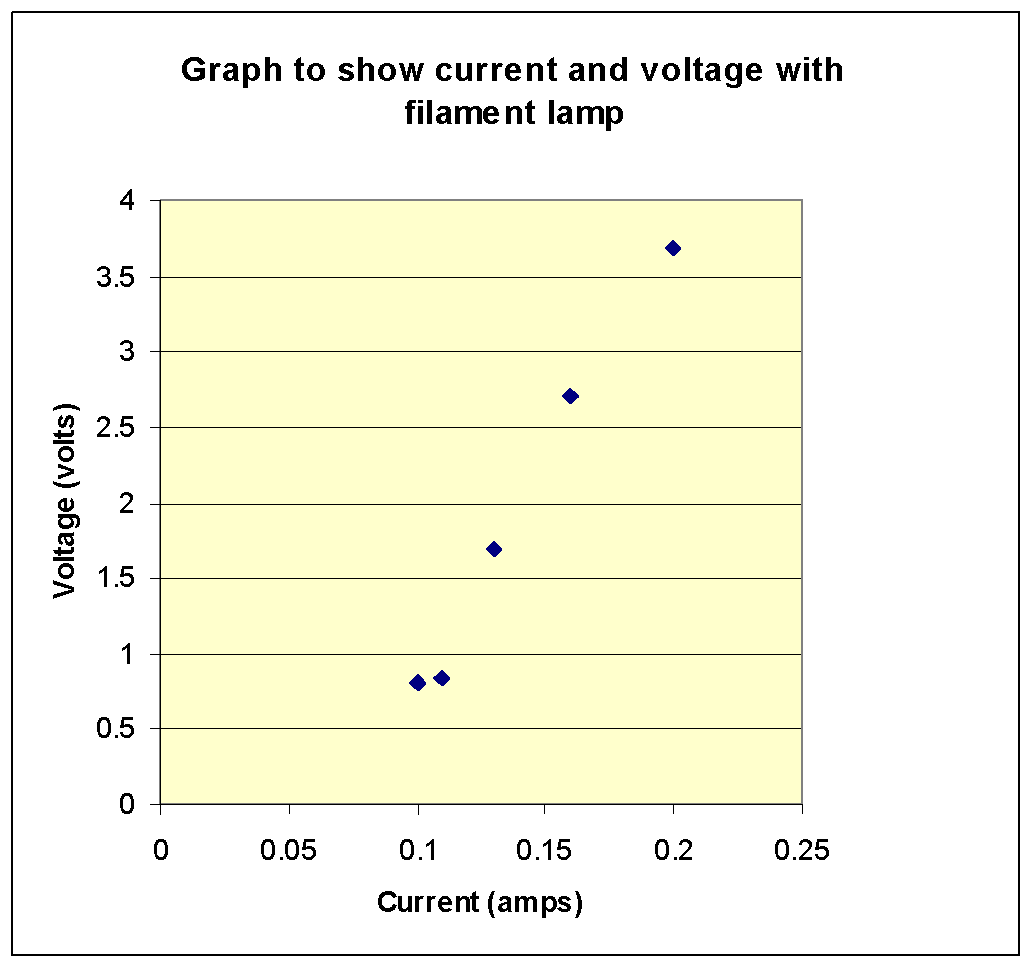
A V I graph for a nichrome wire is given below. What do you infer from this graph? Draw a
The nickel-chromium system reveals that chromium is fairly soluble in nickel. It has a maximum soluble rate of 47% at eutectic temperature, which then decreases to approximately 30% at room temperature. Several commercial alloys are based on this solid solution. These alloys have superior resistance to high-temperature corrosion and oxidation.

Properties of Nichrome Wire Science Struck
The temperature coefficient of resistivity is an empirical quantity that shows the relationship between a change in the resistance or resistivity of a material with the temperature of that material (Boundless, n.d.). Nichrome, a non-magnetic alloy, is usually composed of 80 percent nickel and 20 percent chromium.
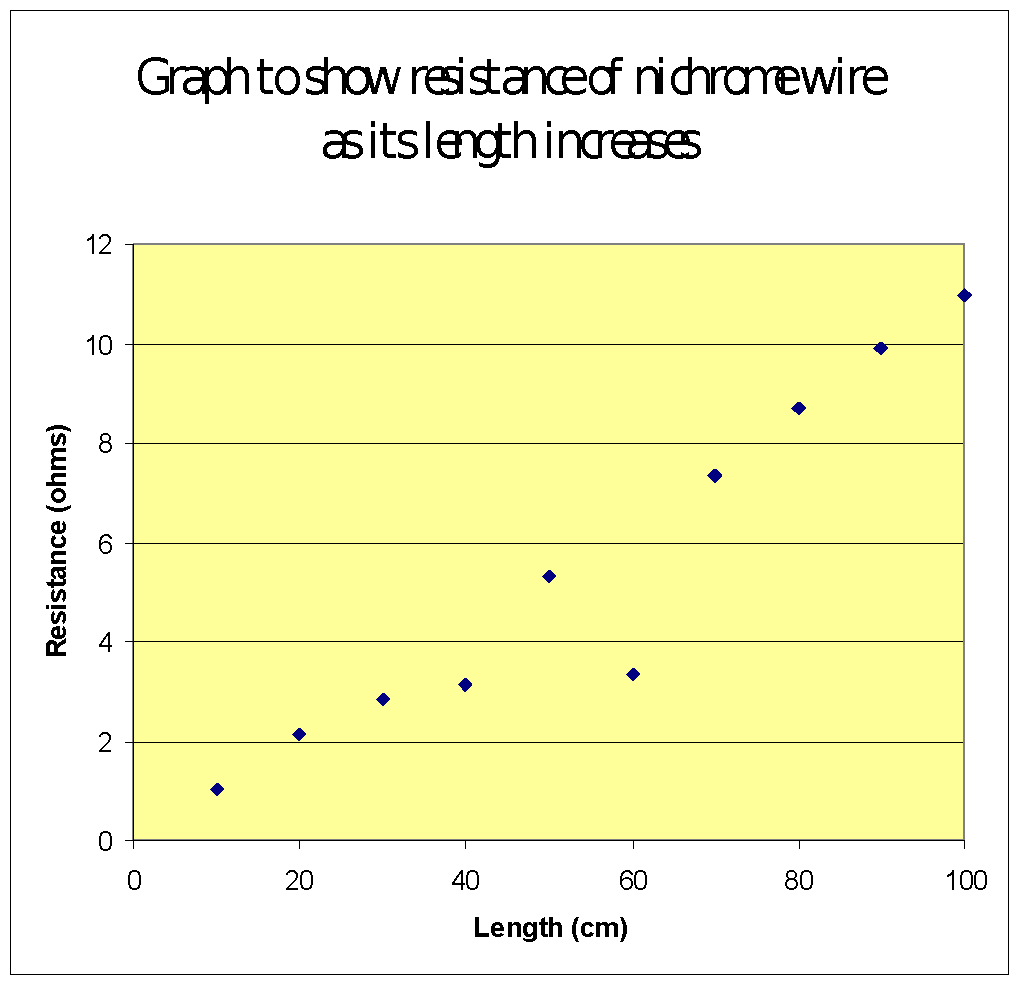
The varying of the resistance of nichrome wire depending on its length ALevel Science
"Nichrome" published on by null. Tradename for a group of nickel-chromium alloys used for wire in heating elements as they possess good resistance to oxidation and have a high resistivity. Typical is Nichrome V containing 80% nickel and 19.5% chromium, the balance consisting of manganese, silicon, and carbon.

Investigate the effects of resistance on a nichrome wire GCSE Science Marked by
The resistivity of a material is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electrical current. The symbol for resistivity is the lowercase Greek letter rho, ρ, and resistivity is the reciprocal of electrical conductivity: ρ = 1 σ. The unit of resistivity in SI units is the ohm-meter (Ω ⋅ m.

⏩SOLVEDWhat is the resistance of a Nichrome wire at 0.0^∘ C if its… Numerade
Nichrome wire is often used as resistance wire, because it's got a high melting point (around $1400^\circ C$) and resists oxidation well. If you pass a current through a Copper wire, it's got a very low resistance and doesn't really heat up unless you pass a very high current, and obviously an insulator which would have a ridiculously high resistance wouldn't heat up at all, since very little.

A portion of Nichrome wire of radius 2.50 mm is to be used in winding a heating coil. If the
Nichrome (also known as NiCr, nickel-chromium or chromium-nickel) is a family of alloys of nickel and chromium. (2,550 °F), and has an electrical resistivity of around 112 μΩ-cm, which is around 66 times higher resistivity than copper of 1.678 μΩ-cm. Almost any conductive wire can be used for heating, but most metals conduct.
12th physics NCERT chapter 3 CURRENT ELECTRICITY short Question Answer NAWENDU CLASSES
Resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. Good electrical conductors have very low resistivities and good insulators have very high resistivities.. Nichrome, a non-magnetic alloy that is commonly made up of 80% nickel and 20% chromium, has a resistivity ranging from 1.10 × 10 −6 Ωm to 1.50.

Nichrome Wire Resistance Chart
This table presents the electrical resistivity and electrical conductivity of several materials. Electrical resistivity, represented by the Greek letter ρ (rho), is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. The lower the resistivity, the more readily the material permits the flow of electric charge.

How the length of nichrome wire affects the resistance GCSE Science Marked by
Analysis of Results. The resistivity, ρ, of the wire is equal to Where: ρ = resistivity (Ω m); R = resistance (Ω) A = cross-sectional area of the wire (m 2); L = length of wire (m); Rearranging for the resistance, R, gives: Comparing this to the equation of a straight line: y = mx