
Life Cycle Of A Plant For Kids All You Need Infos
Plants are classified by the number of growing seasons required to complete their life cycle. Generally, these groups are annuals, biennials, and perennials. Annuals will provide continuous blooms throughout the growing season, while biennials provide blooms during their second year of growth. Perennials will bloom for 2 to 8 weeks or longer.
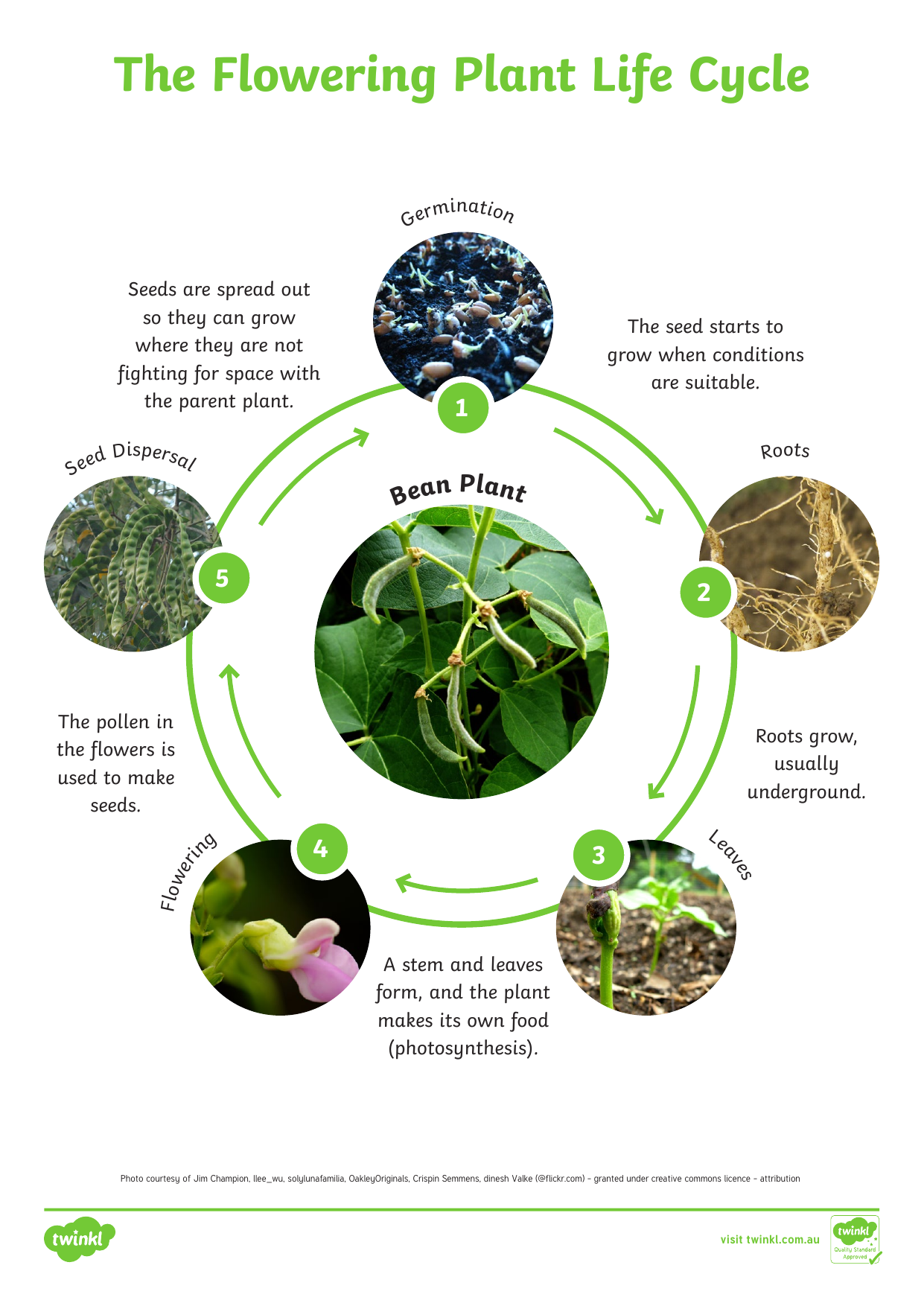
aut2s121floweringplantlifecycle ver 2
A biennial requires all or part of two years to complete its life cycle. During the first season, it produces vegetative structures (leaves) and food storage organs. The plant overwinters and then produces flowers, fruit and seeds during its second season. Swiss chard, carrots, beets, sweet William and parsley are examples of biennials.
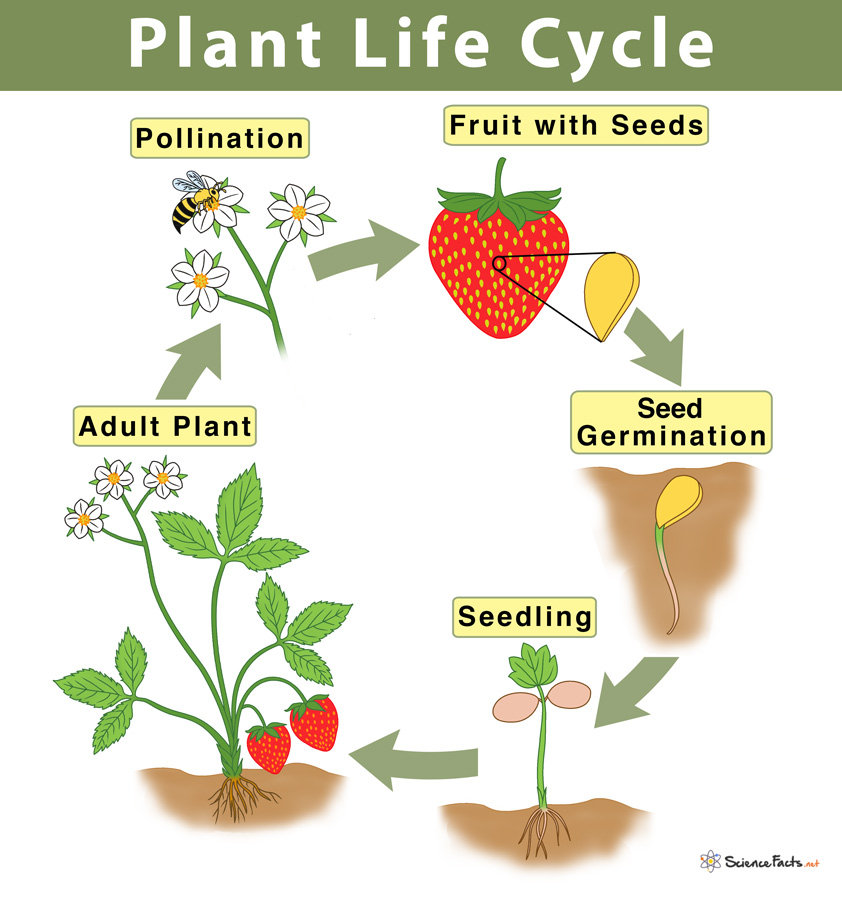
Plants Life Cycle (L) South Huntington Public Library
Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. The haploid gametophyte produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. Fusion of the male and females gametes forms the.

Life Cycle Of A Flower Apple For The Teacher Ltd
Biennials are plants that take 2 years to go through their life cycle. They grow from a seed, then rest over winter. In spring, they produce flowers, set seeds and die. New plants grow from the seeds. Perennials are plants that live for 3 or more years. Some, such as trees, flower and set seeds every year for many years.

Flowering Plants Have A Life Cycle All About Cwe3
Flowers come from seeds, and they create seeds too. All flowering plants go through the following life cycle. Germination is the process by which a plant begins to grow from a seed. Roots form.
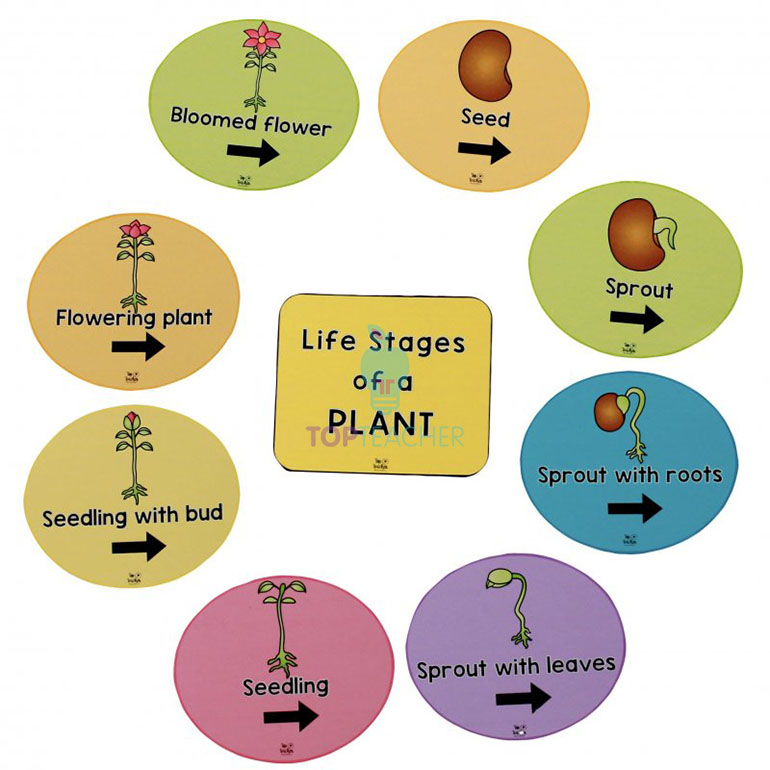
Life Cycle of a Plant Top Teacher
A flowering plant (Heliconia bihai) in its sporophyte phase (In its gametophyte phase, a flowering plant may consist of just a few cells). Plant sexual reproduction is different from animal sexual reproduction in that it uses a system known as the alternation of generations, in which there are two generations per life cycle.. Plants in one generation are diploid, which means that their cells.
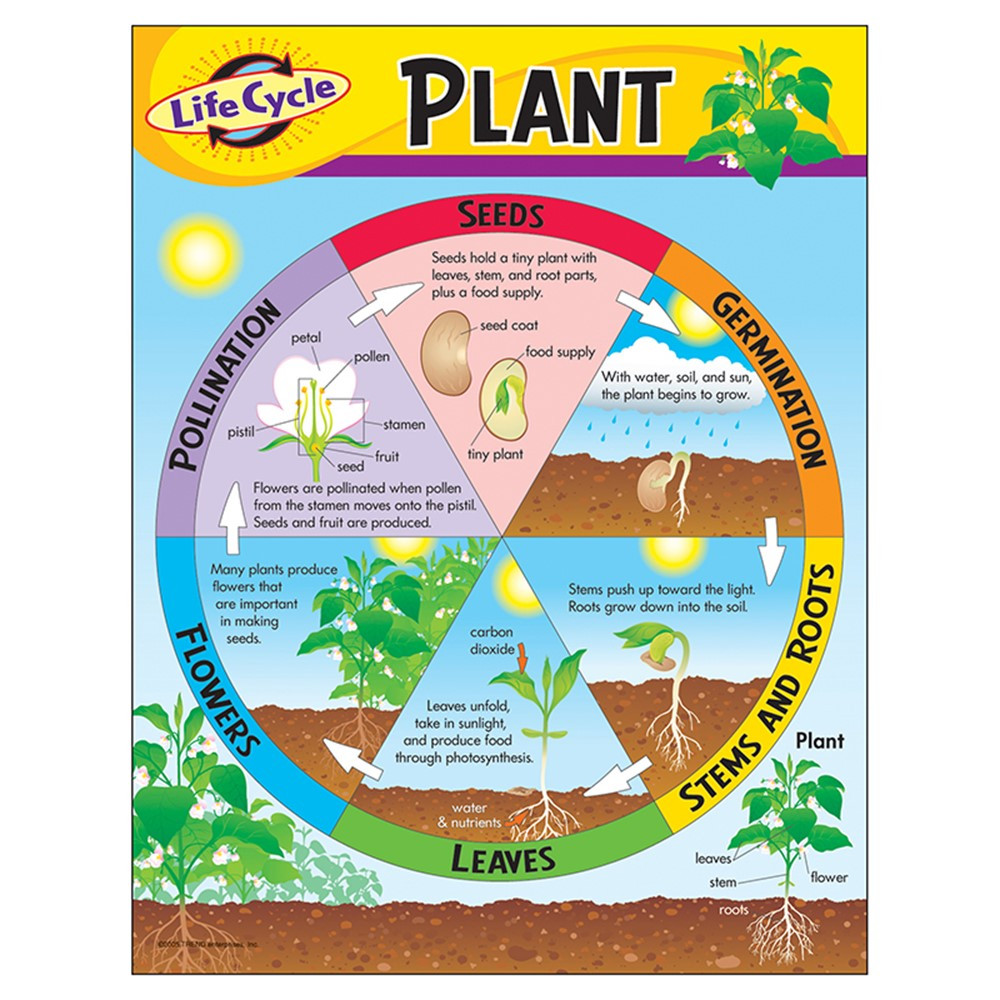
Life Cycle of a Plant Learning Chart, 17" x 22" T38179 Trend Enterprises Inc. Science
A basic plant life cycle goes through five stages: 1) seed, 2) seed germination, 3) seedling, 4) adult plant, and 5) pollination and fertilization. They are discussed below in detail. 1) Seed. The life cycle of a flowering plant begins with a seed. It has a protective outer covering called the shell. Inside the shell contains the baby plant or.
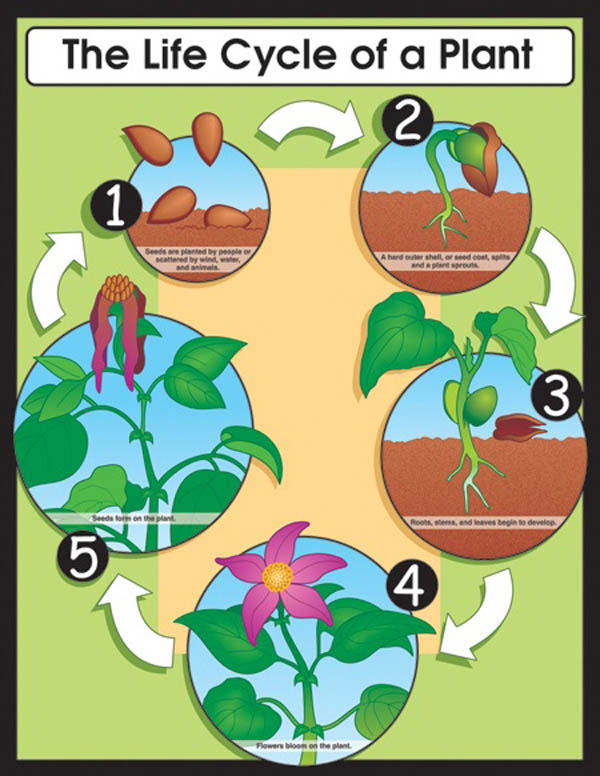
Life Cycle of a Plant Chartlet CarsonDellosa
Seed Dispersal. 1. Seed -. The plant life cycle starts with a seed. From the outside, seeds are protected by a tough layer, called Outer Coat. But inside every seed, there is a tiny baby plant, known as an embryo. The embryo has a root, shoot as well as the first true leaves. Seeds wait to germinate until three needs are met:- water, correct.
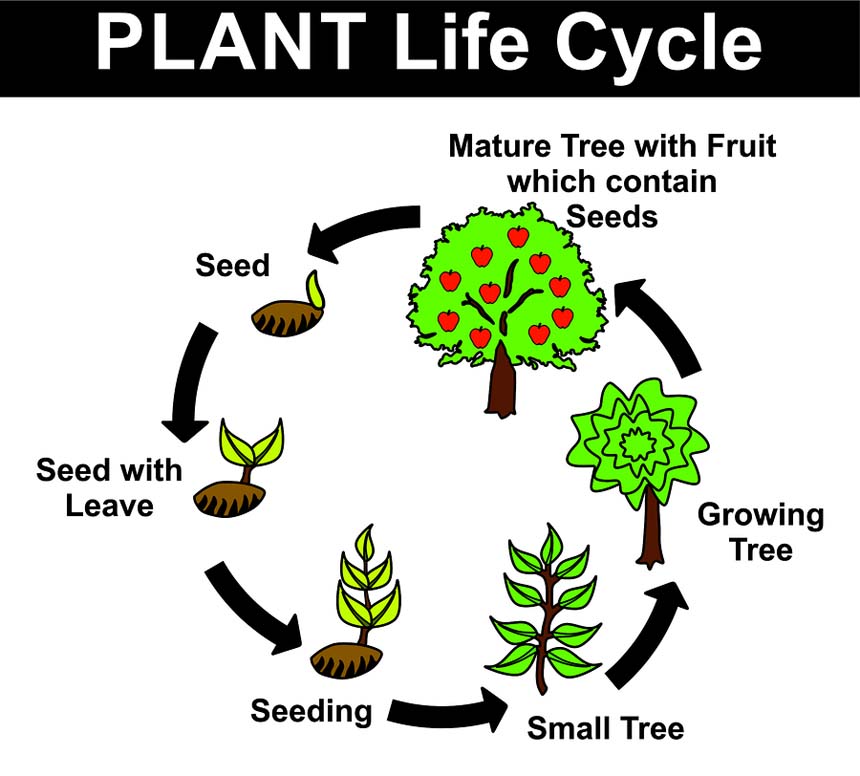
Growth clipart plant lifecycle, Growth plant lifecycle Transparent FREE for download on
Join Ms Tree as she walks down memory lane through the stages of the plant cycle, to see how she transformed from a seed to a beautiful plant that bears frui.
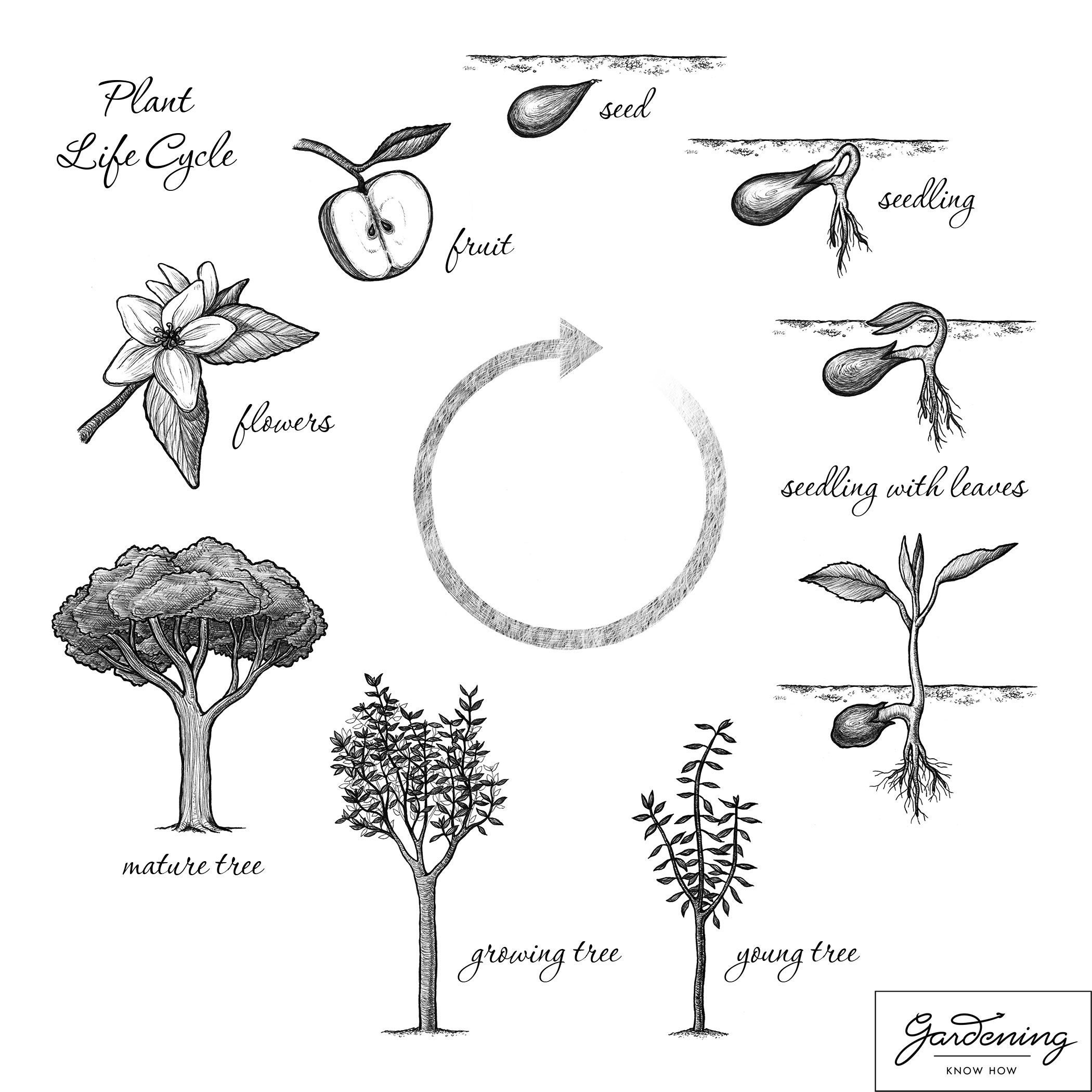
Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How
General Plant Life Cycle. The life cycle of all plants is complex because it is characterized by alternation of generations. Plants alternate between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte generations, and between sexual and asexual reproduction. The ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually gives plants the flexibility to adapt to.
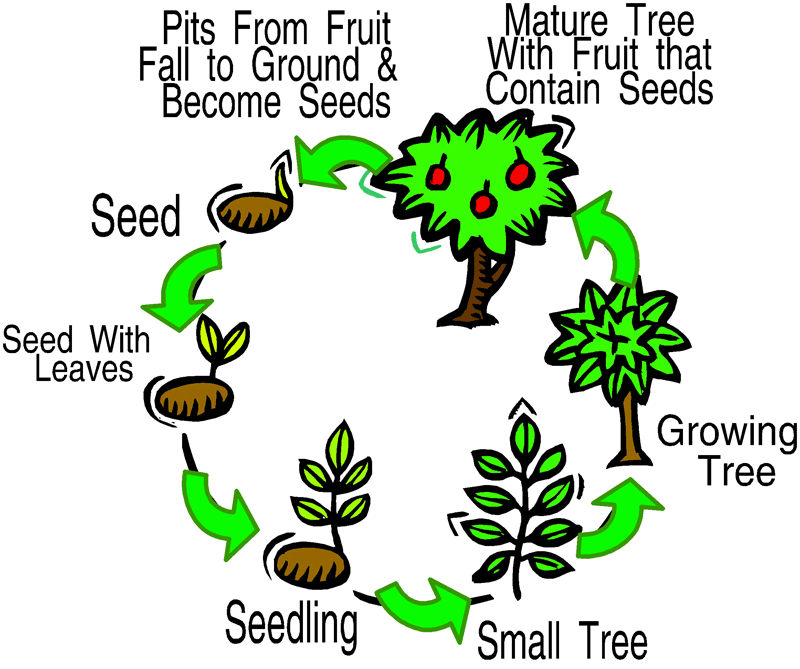
Science Life Cycle of Plant
Describe the two stages of a plant's lifecycle. Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. The haploid gametophyte produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures.

Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant Chart Australian Teaching Aids Merit and Award Classroom
The stages of a plant's life cycle are broken into 3, 4, and 5. But the most widely accepted is the 5 stage model. The five stages of the Life cycle of Plants are: Seed. Germination and Seedling. Growing to Maturity. Flowering, Pollinating, and Seeding. Seed Dispersion.

Agriculture and the Plant Life Cycle Farm Credit of the Virginias
Plants exhibit haplodiplontic life cycle wherein the gametes (sex cells) are not a direct product of meiosis. Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. Throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. This cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. In.

Plant Cycles For Kids Plant Life Cycle Unit For Kindergarten First By Danielle Murphy Shimmer
The life cycle, on the other hand, is the sequence of stages a plant goes through from seed germination to seed production of the mature plant. Some plants, such as annuals, only need a few weeks to grow, produce seeds and die. Other plants, such as the bristlecone pine, live for thousands of years. Some bristlecone pines have a documented age.
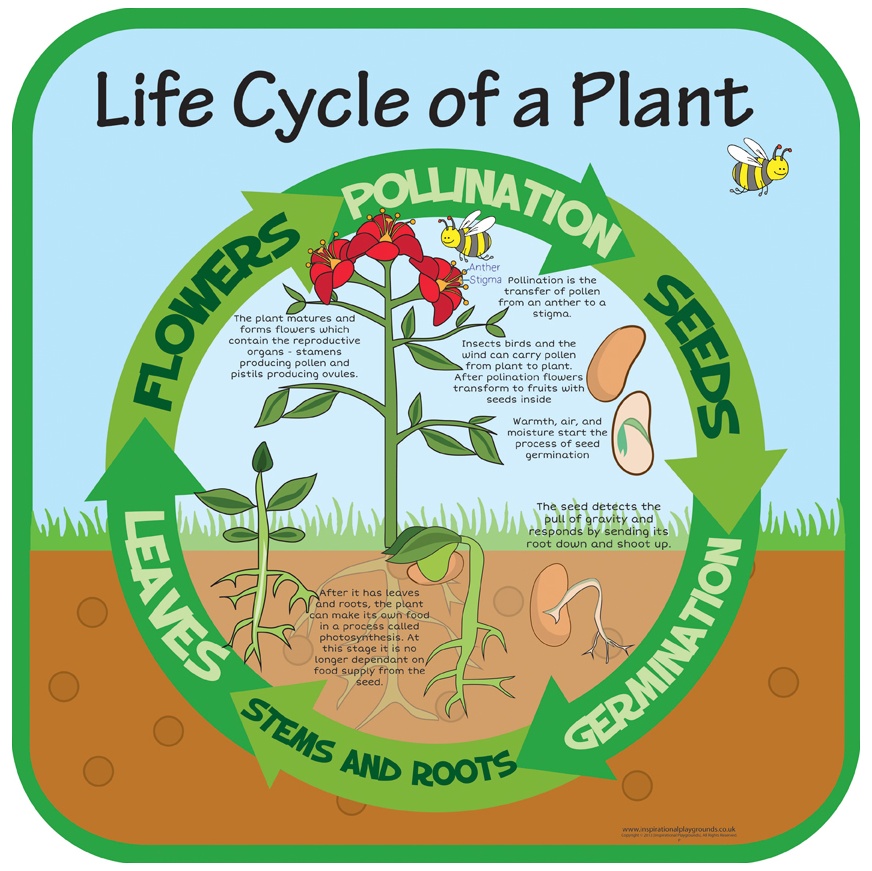
Life Cycle Of A Plant Sign
The ovules, located in the stigma, contain the other half. When the pollen reaches the ovules of a plant, they are fertilized and become seeds. Then, the plant's fertilized seeds are dispersed by wind, water, or animals, and the whole process begins again. Cite this Article. The plant life cycle consists of five stages, from seeds to growth to.
.png)
Agriculture and the Plant Life Cycle Farm Credit of the Virginias
A typical plant's life cycle is diagrammed in Figure below. L ife Cycle of Plants. Th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. Early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. Spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need.
- Bottle Shop Blues Point Road
- William And Kate A New Royal Family
- The Last Ship Season 6
- 141 Old Castle Hill Road
- Nsw Department Of Enterprise Investment And Trade
- Out And About Festival Perth
- China Club Central Hong Kong
- Turbo Outback Truckers Where Are They Now
- Ronnie Coleman Before Body Building
- Fire Force Season 3 Release Date