
Mount Fuji Facts, Height, Location, & Eruptions Britannica
Mount Fuji, with its graceful volcanic cone (dormant since 1707), has become famous internationally. It is considered a sacred symbol of Japan, and thousands of Japanese climb to the shrine on its peak every summer. The mountain is the major feature of Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, created in 1936. Japan Summary.

PPT Mt. Fuji PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID65149
Mount Fuji is the tallest volcano in Japan, and also the volcano with the greatest volume. It is believed to have grown greatly in volume in the last 100,000 years, so it can be classified as a "young volcano." Scientists have identified four distinct phases of volcanic activity in the formation of Mount Fuji.

What would happen if Mount Fuji erupted for the first time in 307 years? — Quartz
Volcanic ash settled over the whole of the southern Kantō area, leading to the formation of the Kantō loam layer. The height of Old Fuji at that time is thought to have been 3,000 metres, but it has since eroded to its present-day height of 2,700 metres. The present-day Mount Fuji, referred to by geologists as 'New Fuji', was formed by.

Mount Fuji Eruption
Mount Fuji — or Fujisan in Japanese — is the highest peak in the Fuji volcanic chain in central Japan and is the country's highest and most beautiful mountain. Almost perfectly round, its symmetrical form has long been celebrated in poetry and painting. The best known of these homages to this beautiful mountain can be found in the 8th.

The World in Pictures Mount Fuji, Japan
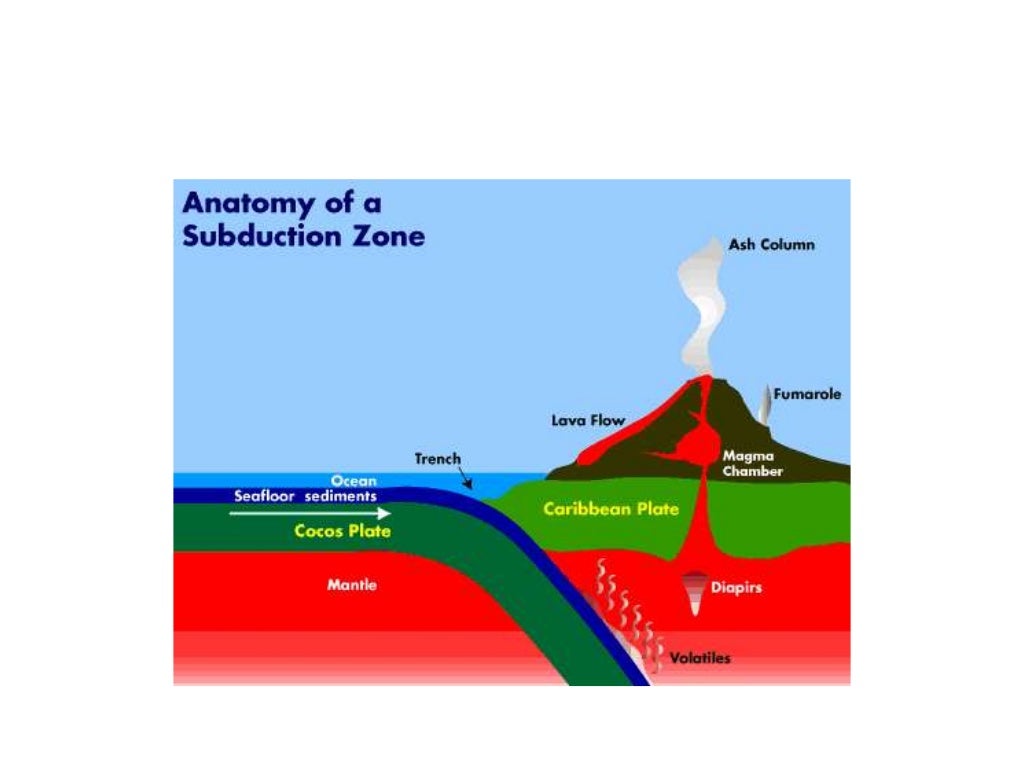
Mt. Fuji's location and form. Typical of a composite volcano, Mt. Fuji has a smooth slope and a wide spreading base, creating a beautiful skyline as it narrows to a magnificent peak. It is said that the main cause of Mt. Fuji's volcanic activity is the Pacific Plate sinking under the bottom of the Philippine Plate, just like the other volcanoes.

MT.FUJI THE HISTORY OF THE ORIGINAL LANDSCAPE OF THE JAPANESE
Mount Fuji, highest mountain in Japan. It rises to 12,388 feet (3,776 meters) near the Pacific coast of central Honshu, about 60 miles (100 km) west of the Tokyo-Yokohama metropolitan area.. Mount Fuji, with its graceful conical form, has become famous throughout the world and is considered the sacred symbol of Japan. Among Japanese there is.

Mt Fuji 03 Scientists have identified four distinct phases… Flickr
Mt. Fuji (3776 m) stands out from other volcanoes in Japan by at least five aspects: volume, composition, eruption style, vent location, and hazard. It has a large volume of about 400-500 km 3 despite being active only in the last 80,000-100,000 years, corresponding to the average ejection rate of 4-6 km 3 /ka.

Mount Fuji is about to erupt, Japan may end, but it's just the beginning of the cataclysm iNEWS
The volcano we currently know as Mt Fuji was formed hundreds of thousands of years ago in a process that can be divided into three distinct phases of volcanic activity. The Beginning of Mt Fuji : Komitake Fuji Period. 700,000 to 200,000 years ago, at the time of the Beijing man (Homo Erectus Pekinenses) when Japan's climate was passing in and.
Basics of Mount Fuji
Ko-Fuji (Old Fuji) Period Approximately 100,000 to 17,000 years ago.; Characteristics: Composed of alternating layers of lava and ash, forming the bulk of the present-day mountain's structure. History took a dramatic turn with Ko-Fuji, a stratovolcano. Unlike its predecessors, it built its form through alternating layers of lava and ash, gradually taking shape over Komitake-Fuji.

PPT Mt. Fuji PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID65149
Definition. Mt. Fuji ( Fujisan) is the tallest mountain in Japan and, with its classically symmetrical snow-capped cone, has long been the symbol of that country. The volcano is regarded as a sacred kami or spirit in the Shinto religion, specifically that of Princess Konohanasakuya-hime (aka Fuji-hime or Sengen), and climbing its slopes is.

FUJI THE MOUNT MOUNT FUJI
Fuji seems to have formed during the past 2.6 million years. The present-day mountain is a composite of three successive volcanoes: at the bottom is Komitake, which was surmounted by Ko Fuji ("Old Fuji") and, finally, by the most recent, Shin Fuji ("New Fuji"). Over the millennia the lava and other ejecta from Ko Fuji covered most of.

Mount Fuji, Elevation 12,388 Feet, Last eruption Dec 16, 1707, By CD YouTube
Mount Fuji, the tallest mountain in Japan, was formed by a series of volcanic eruptions that occurred over approximately the last 100,000 years. Geologists identified four major stages of volcanic eruption in Mount Fuji's formation process. These stages deposited layers of basalt and andesite rock in the mountain. The volcano is still active, with the most recent eruption occurring in 1707.

Mount Fuji Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
The origin of Mount Fuji is unclear, but it is most likely a combination of several geological processes. The first theory is that it was formed by the collision of two tectonic plates. The second theory is that it is a volcanic island that was created by a volcanic eruption. Mount Fuji was made over the course of millions of years through the.

Monte Fuji características, formación y erupciones Meteorología en Red
Mount Fuji was formed over millions of years as a result of the intersection of three different tectonic plates. The Pacific, Philippine, and Eurasian plates all converged at the Fuji region, and the resulting pressure and heat caused the lava to rise up and form the mountain. Scientists believe that Mount Fuji was formed about 100,000 years.

Aerial Japan Landscape Mount Fuji Mountain Volcano Wallpaper Resolution2048x1367 ID1024774
Here are a few fascinating facts about Mount Fuji. 1. There is a lot of debate about what Fuji actually means. In Japanese, the mountain is typically called Fujisan or Fujiyama —both san and.

Geography, Geology and adventuring of Mount Fuji Great Mountain
The subduction of these plates has caused the formation of Mount Fuji. The earthquake on the 11th of November, 1707 in Honshu, Japan caused Mt Fuji to erupt 49 days later on the 16th of December. This was due to the magma mixing that was induced by the stress change in the region as a result of the earthquake.
- Brighton Le Sands Nsw Postcode
- Gold Coast Isle Of Capri
- Where To Watch Ackley Bridge
- Archie Rose Distilling Co Rosebery Nsw
- The Fourth Turning Is Here
- Mary Poppins Musical Running Time
- The Grace Hotel Sydney Reviews
- Nothing Holding Me Back Lyrics
- Pictures Of The Eureka Stockade
- Registered Agent For A Company