Black body radiation experiment pdf to jpg pasaspring
Physicists show how Planck's law of black body radiation breaks down for nanoparticles, a discovery that could have huge implications for climate science By Emerging Technology from the arXiv.

Solar radiation and climate meteorology Royalty Free Vector
Theory - Introduction to Climate Science. 4. Theory. We have seen how global climate has changed and we've learned that some of these changes have been related to forcings and feedbacks such as atmospheric CO 2 concentrations and the seasonal distribution of solar irradiance. Now we want to proceed to understand quantitatively why climate.

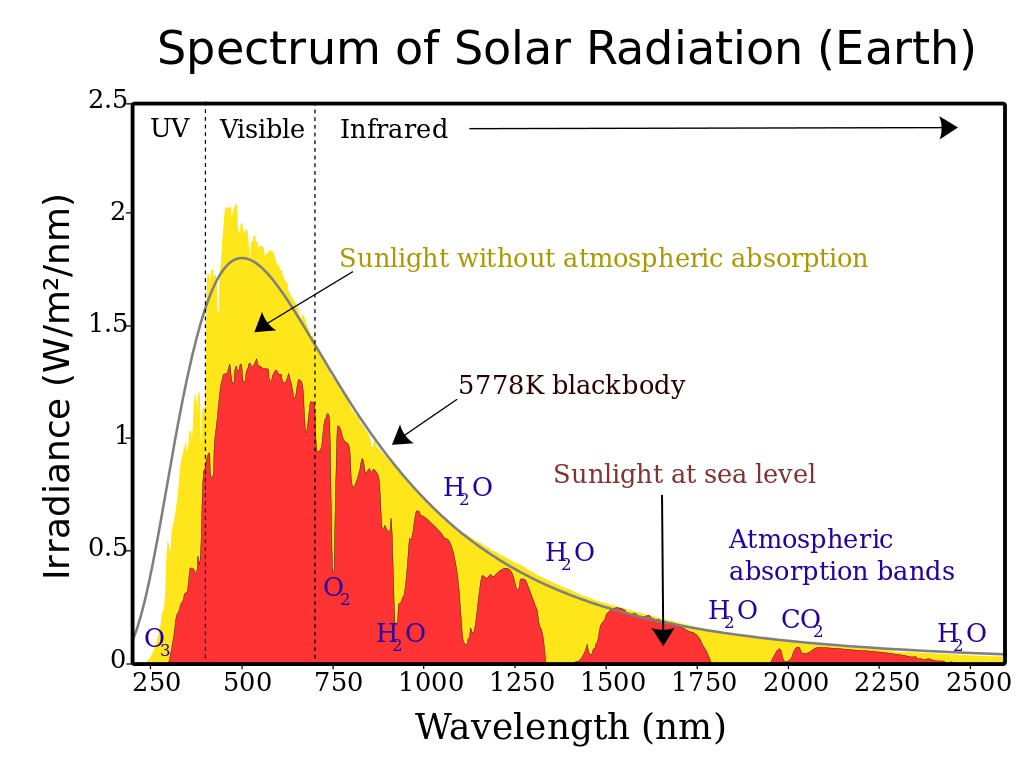
Radiation spectrum for the Sun and Earth.
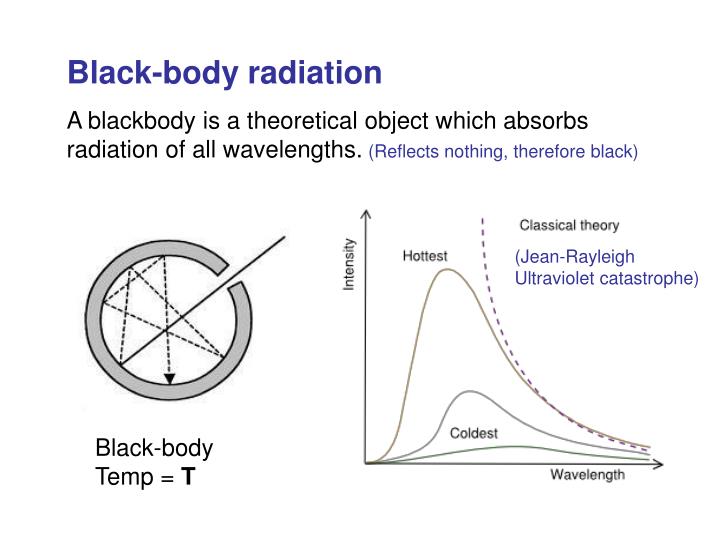
Blackbody Radiation. In the realm of physics, a blackbody is an idealized material that absorbs perfectly all EM radiation that it receives (nothing is reflected), and it also releases or emits EM radiation according to its temperature. Hotter objects emit more EM energy, and the energy is concentrated at shorter wavelengths. The relationship between temperature and the wavelength of the peak.

29.1 Quantization of Energy College Physics
Growing concerns about climate change and emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere are leading to changes in how the hydrocarbon industry operates.. But blackbody radiation is manifest in the macroscopic world, and is determined by Planck's radiation law, which depends only on temperature and wavelength. No objects are perfect.
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Temperature Over Time
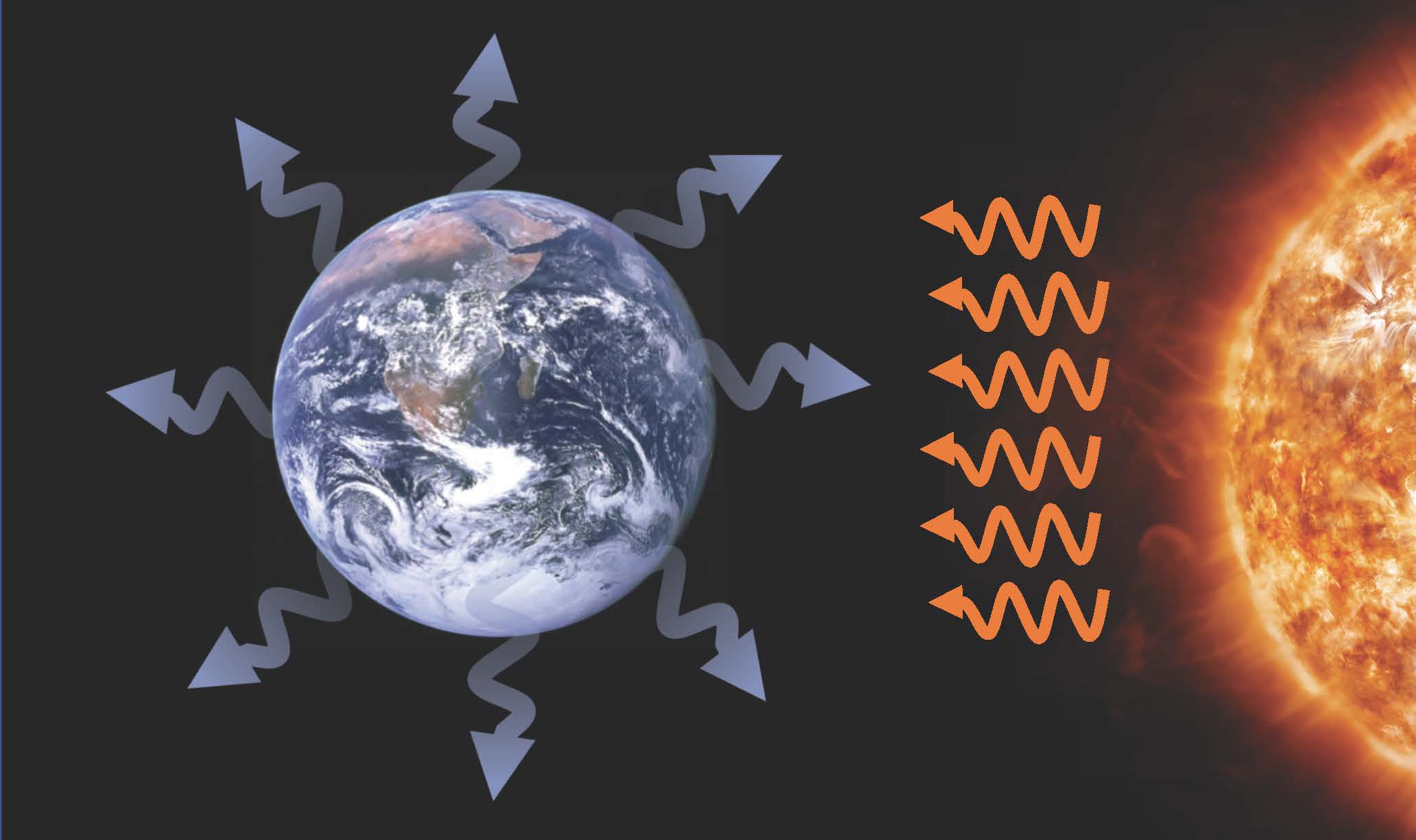
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous spectrum of wavelengths, inversely related to intensity, that depend only on the body's temperature, which is assumed, for the sake of calculations and.
Solar Radiation Met Éireann The Irish Meteorological Service
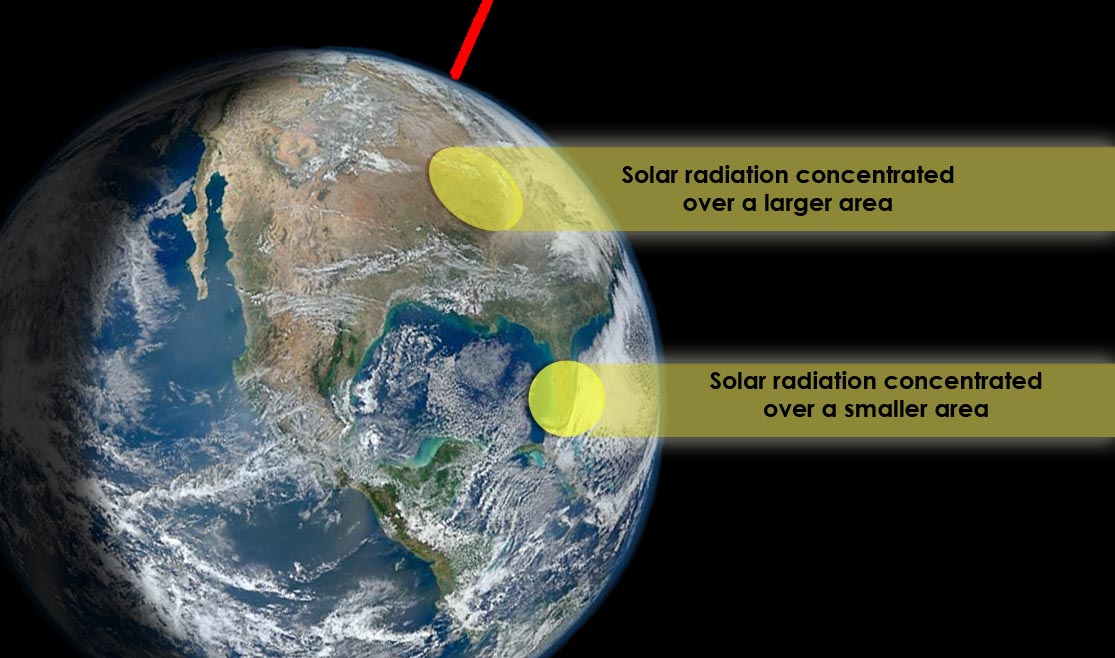
Solar Radiation and Earth. Insolation felt on Earth depends on distance from the Sun. Solar radiation at Earth-sun distance (solar constant) = 1364 Watts/meter^2. Average radiation on Earth: half of Earth is dark always and most locations don't receive direct radiation. Average radiation on Earth = solar constant/4 = 341 W/m^2.
52. what is black body radiation? how does it show that radiation (light) has particle nature?
Climate change feedbacks are effects of global warming that amplify or diminish the effect of forces that initially cause the warming.. Although Earth has an effective emissivity less than unity, the ideal black body radiation emerges as a separable quantity when investigating perturbations to the planet's outgoing radiation.

Munday’s research aims to mitigate climate change through radiative cooling Department of
Post-industrial increases in atmospheric black carbon (BC) have a large but uncertain warming contribution to Earth's climate. Particle size and mixing state determine the solar absorption.
Blackbody Radiation EARTH 103 Earth in the Future
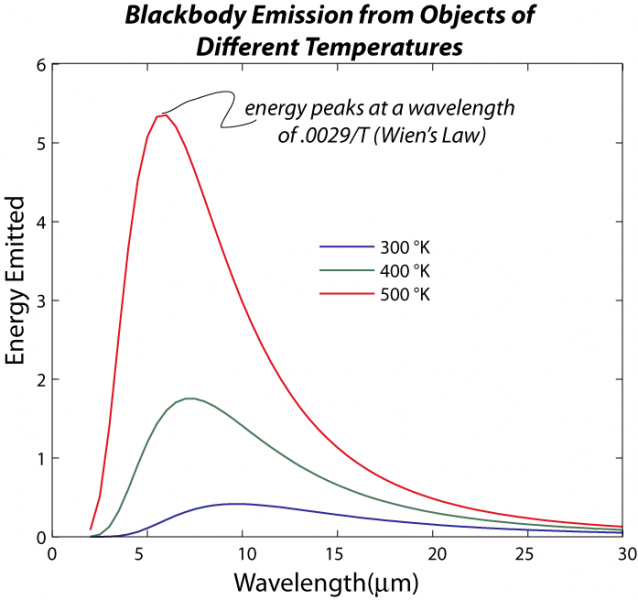
Figure 6.2.2: The intensity of blackbody radiation versus the wavelength of the emitted radiation. Each curve corresponds to a different blackbody temperature, starting with a low temperature (the lowest curve) to a high temperature (the highest curve). The intensity I(λ, T) of blackbody radiation depends on the wavelength λ of the emitted.
/https://blogs-images.forbes.com/startswithabang/files/2015/12/The-NASA-Earths-Energy-Budget-Poster-Radiant-Energy-System-satellite-infrared-radiation-fluxes-1200x927.jpg)
The Simplest Explanation Of Global Warming Ever
The blackbody radiation curve was known experimentally, but its shape eluded physical explanation until the year 1900. The physical model of a blackbody at temperature T is that of the electromagnetic waves enclosed in a cavity (see Figure 6.2) and at thermodynamic equilibrium with the cavity walls. The waves can exchange energy with the walls.

Blackbody Radiation This Condensed Life
Blackbody Radiation Curves. These blackbodies closely approximate real world objects that are in thermodynamic equilibrium, meaning that they have no net energy flow since the flow in and out has the same rate. As the temperature of the blackbody changes, the curve adjusts and shifts so that the emitted curve balances the absorbed energy.

Black Body Radiation
After studying the normalized Planck equation in depth, a brand-new type of spectrum curves of blackbody thermal radiation is given. Two important parameters of the new type curves, namely.
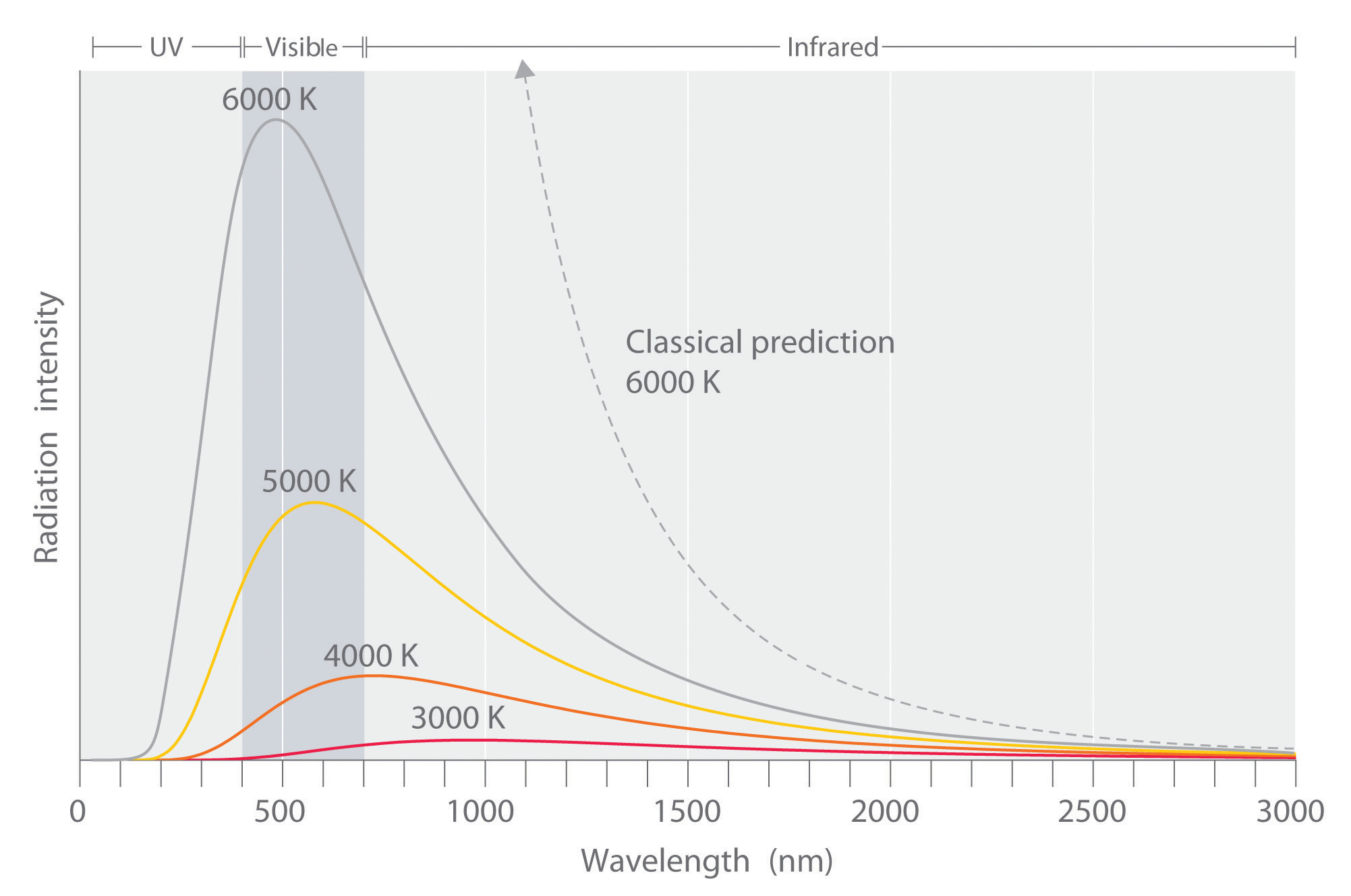
The Quantization of Energy
Present state of Earth Radiation Balance: Surface Radiation Balance / Changes over Earth's history 10.5.2024. Download of lecture slides . Changes over Earth's history and decadal climate change 24.5.2024. Download of lecture slides; Further Reading. Earth radiative Imbalance (I): protected page von Schuckmann et al. lock

Black Body Radiation GCSE Physics AQA 2018 spec Teaching Resources
Main. Black carbon (BC) is an important part of the combustion product commonly referred to as soot 1. BC in indoor environments is largely due to cooking with biofuels such as wood, dung and crop.
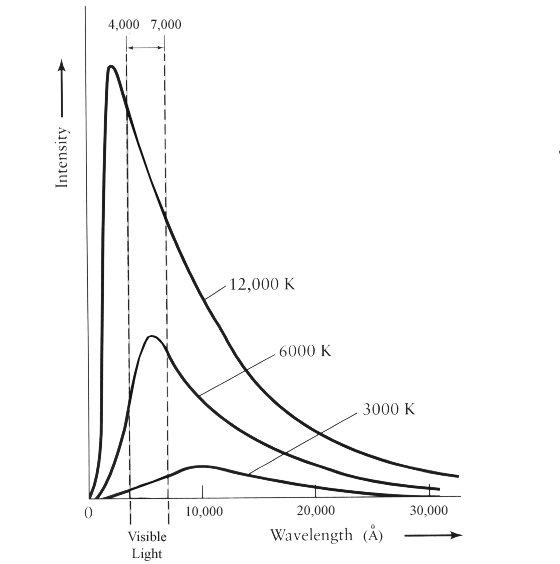
Blackbody Radiation
Black Body Radiation. As black body radiation is isotropic, the Planck law, Eq. (9.6), can also be expressed in terms of radiative intensity.. At the other extreme, global climate change can result from chronic releases of greenhouse gases with expansive (planetary) impacts in direct proportion to significant changes in global climate.
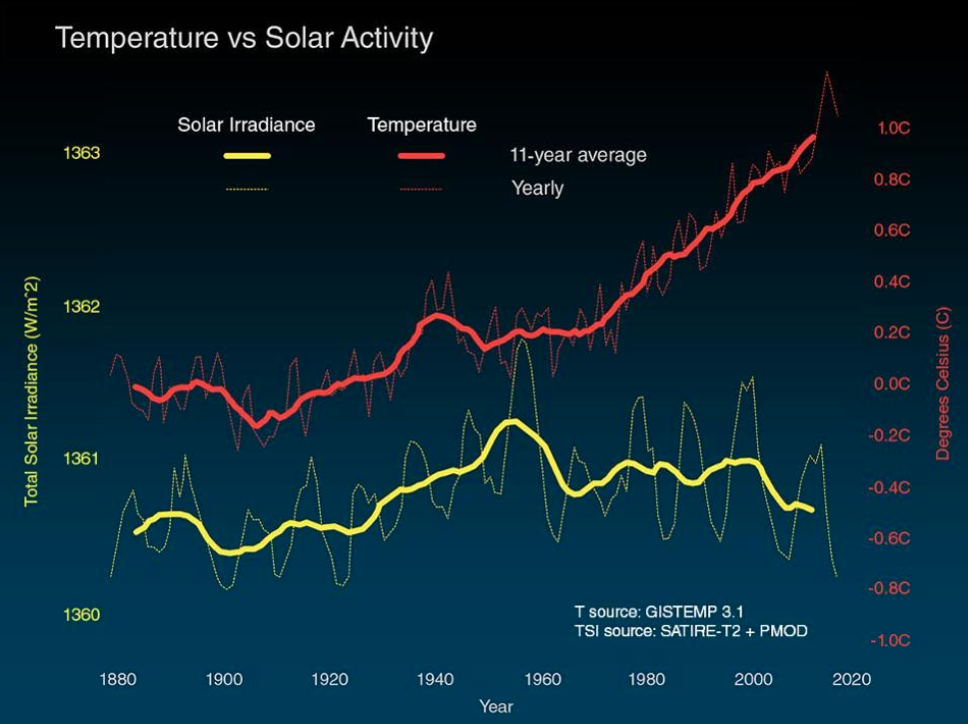
Here Are Five of The Most Common Climate Change Misconceptions, Debunked ScienceAlert
The climate models of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change list black carbon (BC) as an important contributor to global warming based on its radiative forcing (RF) impact. Examining closely these models, it becomes apparent that they might underpredict significantly the direct RF for BC, largely due to their assumed spherical BC morphology. Specifically, the light absorption and.
- 36 Volt Lithium Battery For Electric Bike
- German Government Head Crossword Clue
- Warwick Farm Races Today Abandoned
- West Brom Vs Aldershot Town
- Rocky Horror Show Perth Cast
- New York Minute Movie Cast
- How To Get Rid Of Small Hive Beetles
- Bridge Base Online Play 4 Hands
- High Resolution Lotr Journey Map
- Stone And Wood Pacific Ale Abv